The nascent crypto and Web3 space presents challenges beyond standard startup survival rates, making success less certain. To help us invest against these challenges, we first need to understand these odds. To do so, we have to look at past investment cycles in a bid to systematically invest in the future.
Brief History of Previous Investment Cycles
Looking back at previous investment cycles in the cryptocurrency market, we can see how the market has evolved and matured over time.
The origins of digital currency can be traced back to the 1980s and the project called eCash. It was not until the launch of Bitcoin in 2008 that the potential of blockchain technology was realised. Bitcoin peaked at around $260 in April 2013, and this ushered in the season of alternative coins and Initial Coin Offerings (ICOs) from 2014 to 2017. While many of these projects did not deliver as promised, Ethereum emerged as a game-changer that helped to further the potential of decentralized blockchain technology. The ICO boom also brought Bitcoin into the spotlight, with mainstream news outlets covering the exponential rise of its price up to $20,000 in December 2017.
After the price frenzy for Bitcoin, the markets corrected, and Bitcoin was down to $3,200 by December 2018. The previous attention and drastic price fluctuations brought regulatory attention to the cryptocurrency and blockchain scene. During this period of time, remaining ICO teams began delivering their promised products, and blockchains with smart contract capabilities allowed for more sophisticated products to be built on-chain.
This brings us to the most recent investment cycle. At this point, institutions and sophisticated investors start to notice the potential value proposition of Bitcoin and other cryptocurrencies. With more investments and liquidity providers in the crypto ecosystem, teams could experiment with various smart contract projects. The “DeFi Summer” began in 2019. This overlapped with the Non-Fungible Token (NFT) frenzy in 2021, where crypto flirted with the potential implementation of mass retail adoption. Rising institutional and retail interest propelled Bitcoin to its all-time high of $68,000 in November 2021.
After all the euphoria, the gradual price depreciation of Bitcoin ultimately led to the subsequent domino fall of Terra and Luna, 3AC, Celsius, and the FTX exchange. During this new “winter” of the crypto market, the BTC price once dropped to as low as $15,800, before gradually recovering to $28,000 per the time of the publication of this thesis in the beginning of May 2023.
Reassessing the Current Web3 Landscape
The previous bull cycle and the current “winter” prove that there is much resilience in the cryptocurrency, demonstrating how the space has evolved. This winter has peeled away the speculative layer, allowing the Web3 community to focus on delivering value. This cycle has also helped to establish new potentials and highlight the importance of the following areas:
- The importance of decentralisation to reduce singular points of failure.
- Multi-chain versus cross-chain future.
- The importance of privacy and self-ownership.
- A growing potential market of sophisticated derivatives products for risk management.
- A potential of mass retail usage through non-financial-focused products.
DWF Ventures Investments Focus
In crypto venture capital (VC), funds distinguish themselves in three main areas:
- Stage of investment.
- Investment verticals.
- Geography.
Stage of Investment
For stages of investments in crypto projects, DWF Ventures will be focusing on the pre-seed to seed rounds. This allows us a front-row view of the innovative ideas attempting to push to boundaries of the Web3 space. Later-stage projects are welcomed only if they consist of a solid team leading at the forefront of their field.
Investment Verticals
The team of DWF Ventures is focusing on three main verticals:
- Crypto derivative protocols. We are particularly interested in DeFi derivative protocols for two primary reasons. Firstly, they have proven to be a perfect fit for crypto users, often being their first interaction with the cryptocurrency space. Many individuals start with buying and selling tokens and then venture into derivatives like crypto perpetuals or options to enhance leverage and returns. Secondly, as part of its parent company, DWF Labs, DWF Ventures can provide synergistic value additions to derivatives protocols, drawing from its trading expertise.
- Consumer crypto. As mentioned earlier, a significant portion of crypto users initially enters the space through trading, primarily driven by profit-seeking motives. However, maintaining user interest becomes challenging when profits wane. Hence, consumer applications, offering additional appeals like social features, tooling, content, and more, hold the potential to retain and attract a broader mainstream audience. It’s important to acknowledge that predicting the exact nature of the future consumer dapps is challenging, given the unpredictable historic evolution of social apps in Web2. Hence, we maintain an open-minded approach to the evolving landscape of crypto, allowing us to adapt to its dynamic nature.
- Data and privacy layer in the Web3 stack. Investment in infrastructure stacks has historically proven highly profitable for most VC funds. However, the world of Web3 technology is complex and always changing, with new terms and categories emerging. To navigate this ever-changing landscape, DWF Ventures has outlined the relevant verticals in the diagram below.
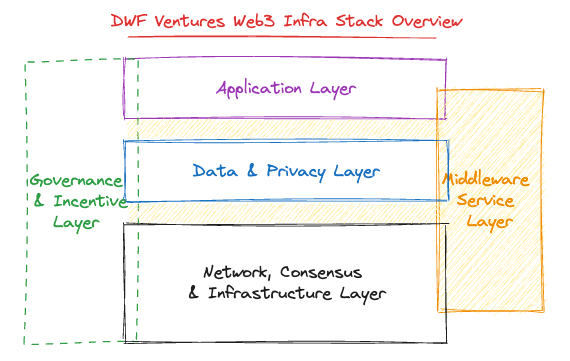
Given the expansive nature of the infrastructure domain, our current focus lies in the Data and Privacy layer. This focus stems from the growing significance of data and privacy, which not only contributes to providing more sophisticated experiences but also broadens the user base for the blockchain space.
Geography
DWF Ventures is the global crypto investment firm covering multiple time zones across key blockchain hubs. Our teams can be found in Switzerland, Dubai, Singapore, Hong Kong, the British Virgin Islands, and Korea.
We believe that whenever there is an internet connection, teams can build in Web3. It is especially relevant for Web3, where teams tend to be decentralised and global. Our geographical mandate spans the globe, covering every region with internet access.
DWF Ventures’ Investment Framework
Based on a study by Coresignal, there were over 490 crypto startups commenced in the first half of 2022. A higher number of projects requires a more rigorous evaluation process. Here at DWF Ventures, we follow a basic investment framework focusing on three main areas:
- Favorable Web3 verticals.
- Project’s level of innovation.
- Compatibility for collaboration on the launch and growth.
Favorable Web3 verticals
DWF Ventures would prefer to focus on the three verticals: Web3 Infrastructure, Crypto Derivative Protocols, and Consumer Crypto Applications.
However, the thought process for picking those verticals is to ensure that the projects have healthy addressable markets and demand. Given that the space is evolving, we are open to corrections and give the benefit of the doubt that new verticals can form over time.
Level of Innovation
In the field of building something completely new, there are different level, and each of them has varying scales of impact. We can classify innovation into four main quadrants:
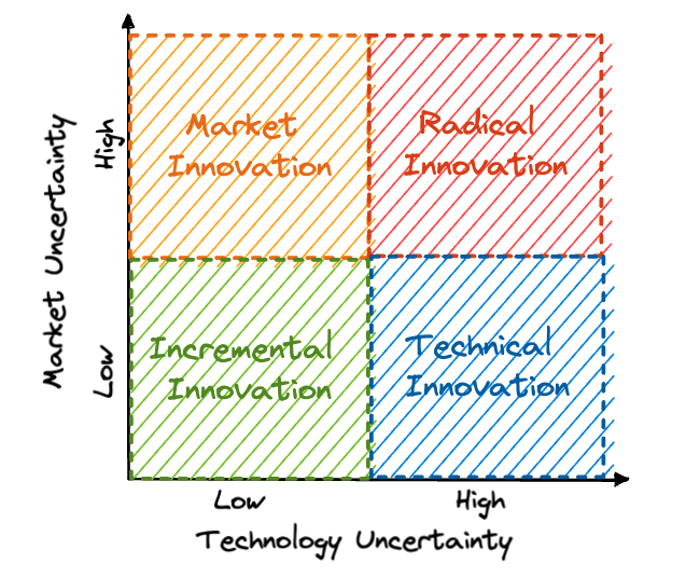
- Incremental innovation. Small and gradual improvements of existing products. For example, a new order type on a decentralised exchange.
- Market innovation. New methods or techniques for pushing a product to the market. Example: the Sushi Swap’s community-driven approach.
- Technical innovation. New and improved versions of existing products. Example: the launch of the Curve stablecoin pools with a new algorithmic formula.
- Radical Innovation. A new product with an entirely novel business model.Example: the launch of Ethereum in 2015.
At DWF Ventures, we typically seek out projects that fall into the realm of market, technical and radical innovation.

Fundamentally, we do not look for projects that will solve the next problem. We want to find startups that will set the next industry standards in their lead vertical. In our opinion, most of the time it is not about solving the next problem, but about creating an irreplaceable want.
Compatibility for Collaboration
According to The Block, an average amount of funds raised by a crypto project has greatly surged in the last two years:
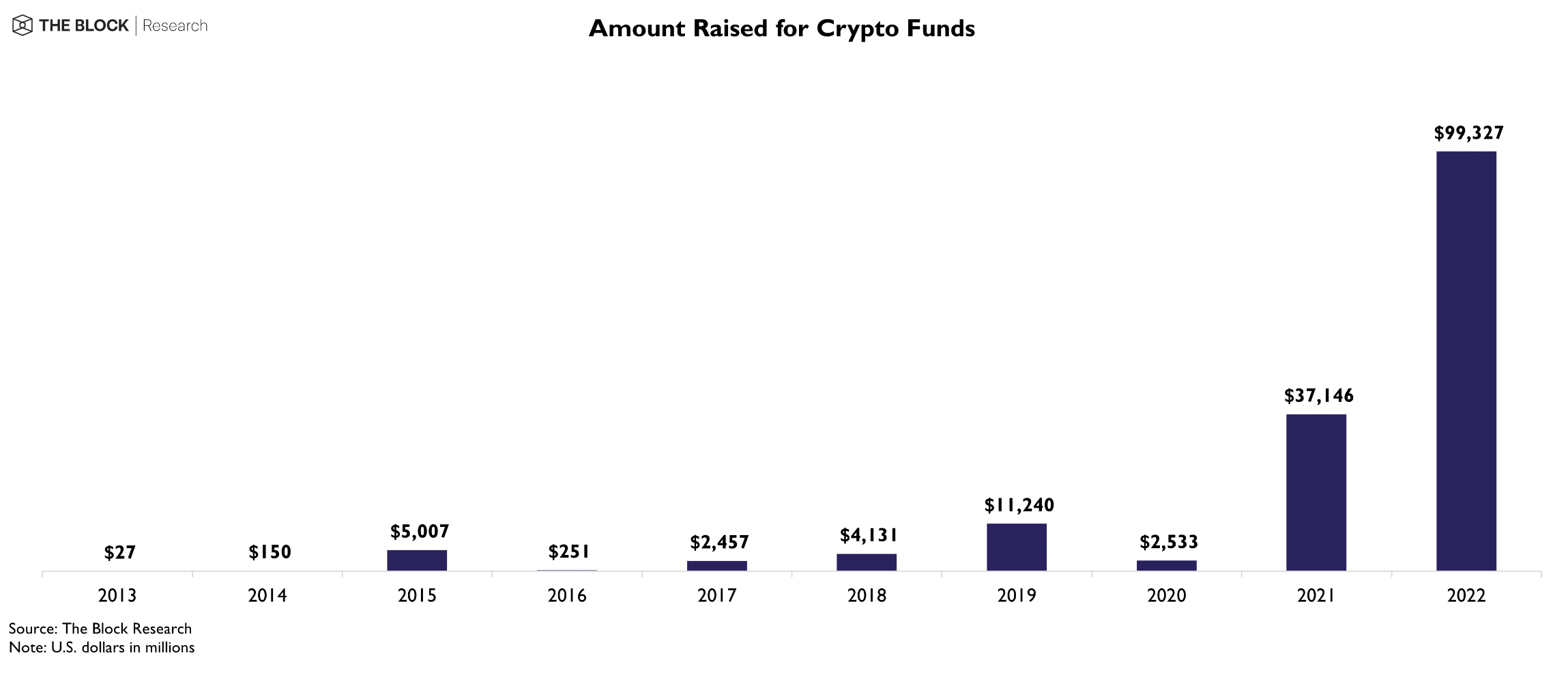
While we can still deploy capital as a sleeping partner, the journey from zero to one is tumultuous, especially in Web3. As investors, we want to provide support that is complementary to the founders’ vision and mission. The areas of support we provide for crypto startups include Go-to-market (GTM) strategies, tokenomics, and even trading expertise.
Ultimately, we believe that crypto venture investment works more as a partnership where both parties are aligned in helping to create value for the space. Therefore, if you’re seeking an investor who shares your vision and a partner committed to building alongside you, reach out to us. Interested parties can pitch their project using the form on the DWF Ventures’s page.



