- Details
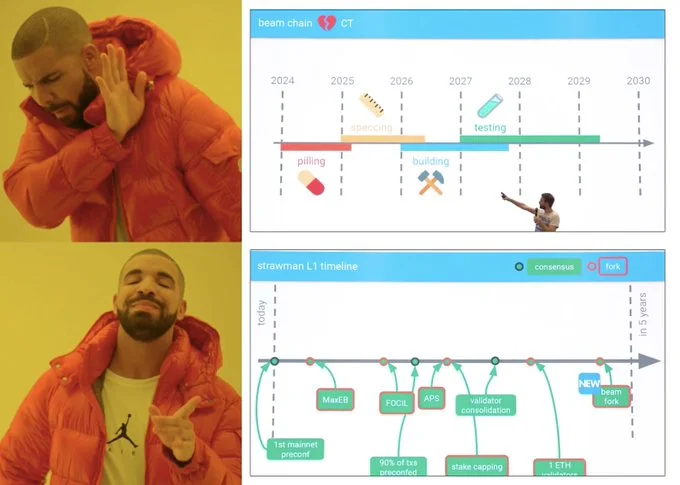
The Beam Chain proposal outlines a comprehensive overhaul of Ethereum's consensus layer. This ambitious initiative aims to modernize the network by integrating advancements in cryptography and addressing existing inefficiencies. However, its extensive five-year roadmap has sparked considerable debate among users and developers.
Before jumping to conclusions on whether the Beam Chain is capable of pushing Ethereum forward, we have to ask ourselves: what exactly does this entail for the blockchain, and what are some possible trickle-down effects?
Background
Announced by Justin Drake at Devcon 2024, the proposal revealed a long-term vision for upgrading Ethereum. Contrary to the perception of being a singular, monumental upgrade, the Beam Chain represents the culmination of multiple targeted enhancements, particularly within the consensus layer.
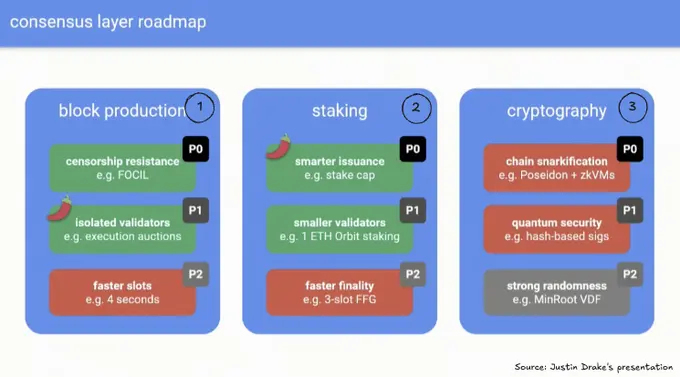
These upgrades are categorised into three primary areas:
- Block Production.
- Staking.
- Cryptography.
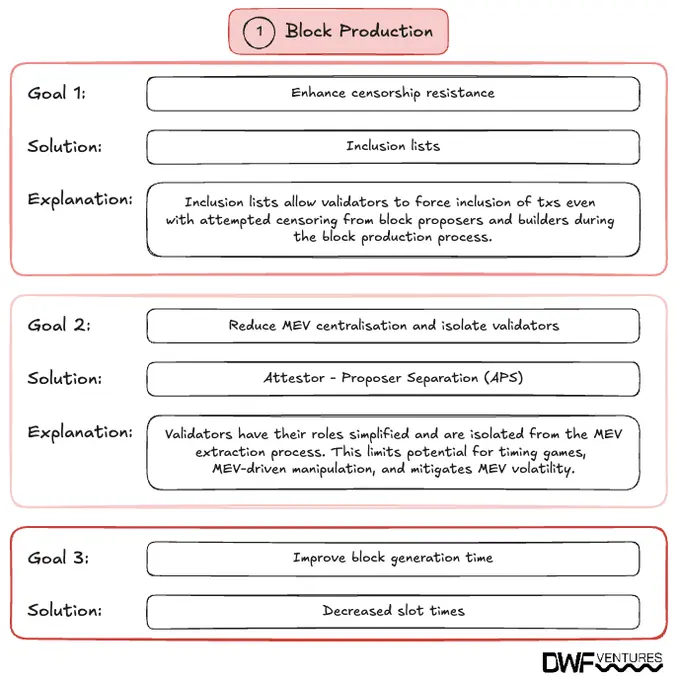
Block Production Enhancements
The proposed changes in block production focus on improving the efficiency and security of how blocks are generated and validated. Key initiatives include:
- Inclusion lists via FOCIL (First-Order Conditional Inclusion Lists). Designed to enhance censorship resistance by ensuring that certain transactions are included in blocks, inclusion lists mitigate the risk of exclusion by block producers.
- Attestor-proposer separation (APS). This mechanism separates the roles of block proposers and attestors to distribute responsibilities more evenly, reducing the potential for centralized control and mitigating risks associated with Maximal Extractable Value (MEV) exploitation.
- Reduced slot times. Shortening the time between block proposals aims to increase transaction throughput and decrease latency, leading to a more responsive network.
Staking Reform and Impact on LSTs
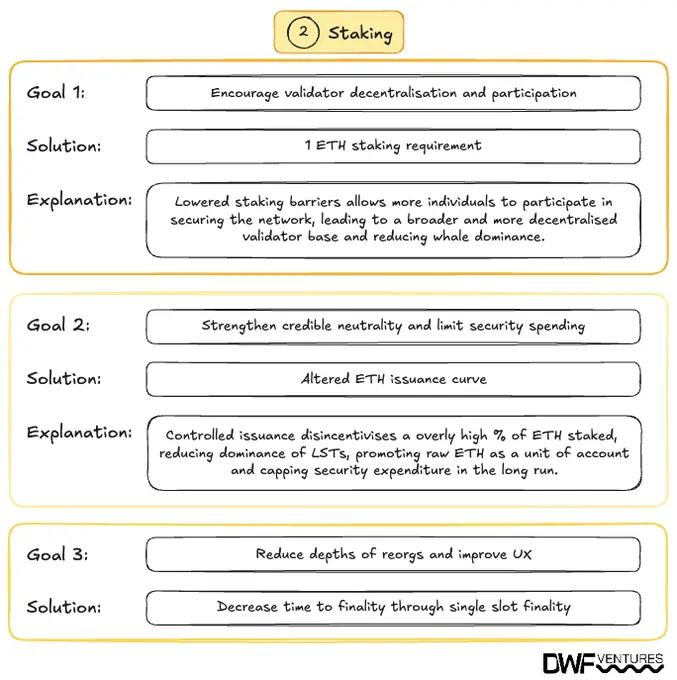
The staking-related proposals aim to promote decentralisation and improve the user experience by implementing the following changes:
- Lowered staking requirements. Reducing the minimum stake from 32 ETH to 1 ETH would democratise network participation, allowing a broader range of users to become validators and thereby enhancing decentralisation.
- Revised ETH issuance curve. Adjusting the issuance rate of ETH aims at aligning incentives more effectively, supporting the network's economic sustainability.
- Single slot finality. Achieving finality within a single slot would significantly reduce the depth of potential chain reorganisations, thereby enhancing security and providing a more predictable user experience.
These changes could have significant implications for large staking entities, particularly Liquid Staking Token (LST) protocols, which currently account for over 60% of Ethereum's TVL.
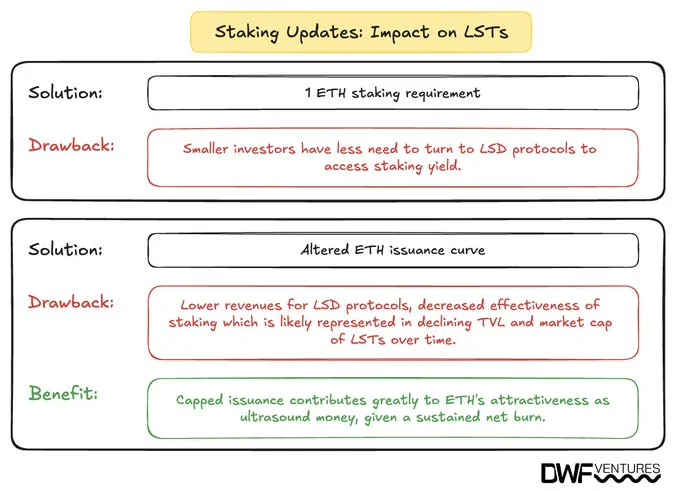
The proposed reduction in staking requirements could lead to a more decentralized staking landscape, potentially diminishing the dominance of large LST providers. With the barrier to solo staking significantly lowered, individual stakers might opt to stake independently rather than through pooled services, impacting the market share and operational models of existing LST protocols.
However, LST platforms offer additional benefits beyond mere access, such as liquidity for staked assets and integration with various DeFi applications. These value-added services may continue to attract users who prioritize flexibility and additional yield opportunities over direct staking.
Altering ETH issuance curve can negatively affect the staking yields, lowering revenue of LSTs. At the same time, it should support ETH’s price performance and contribute to its attractiveness as ‘ultrasound money’.
Cryptographic Advancements
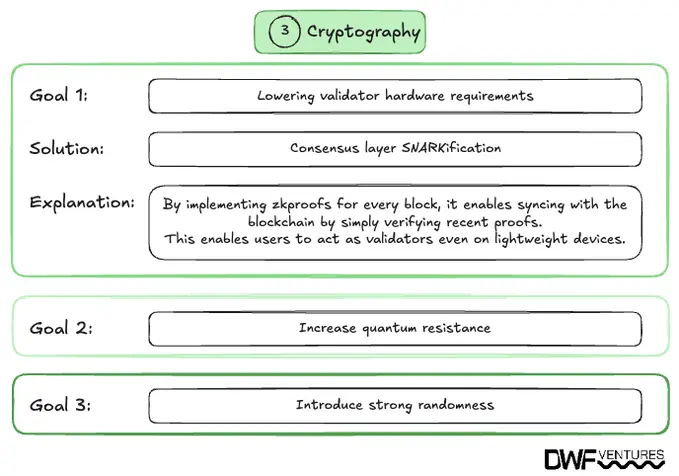
Besides block production and staking, the Beam Chain proposal emphasises the integration of advanced cryptographic techniques, namely:
- Lowering validator hardware requirements. Implementing more efficient cryptographic algorithms would reduce the computational burden on validators, making participation more accessible.
- Enhancing quantum resistance. Incorporating post-quantum cryptographic methods aims to future-proof the network against potential threats posed by quantum computing advancements.
- Stronger randomness. Utilising Verifiable Delay Functions (VDFs) like MinRoot would generate unbiased and unpredictable randomness, which is crucial for secure protocol operations.
Introduction of SNARK
Additionally, the concept of ‘SNARKification’ involves applying succinct non-interactive arguments of knowledge (zk-SNARK) to enable synchronous, programmable execution sharding. This advancement would allow developers to deploy customisable zero-knowledge virtual machines (zkVMs) with greater ease, potentially narrowing the gap between zk-rollups and optimistic rollup solutions in terms of TVL and adoption.
Execution and Data Layer Considerations
While the Beam Chain proposal primarily targets the consensus layer, it operates together with planned enhancements to Ethereum's execution and data availability (DA) layers. Notably, Drake also mentioned plans to increase gas limits by up to 100 times and develop zk-execution clients that consume minimal resources. On the DA side, initiatives like danksharding aim to exponentially increase the number of data blobs per second, further scaling the network's capacity.
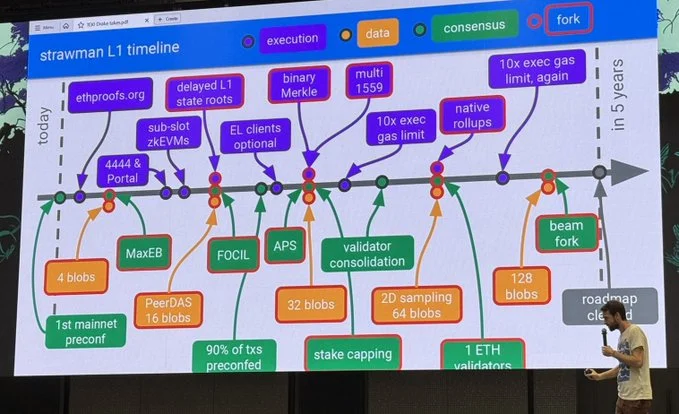
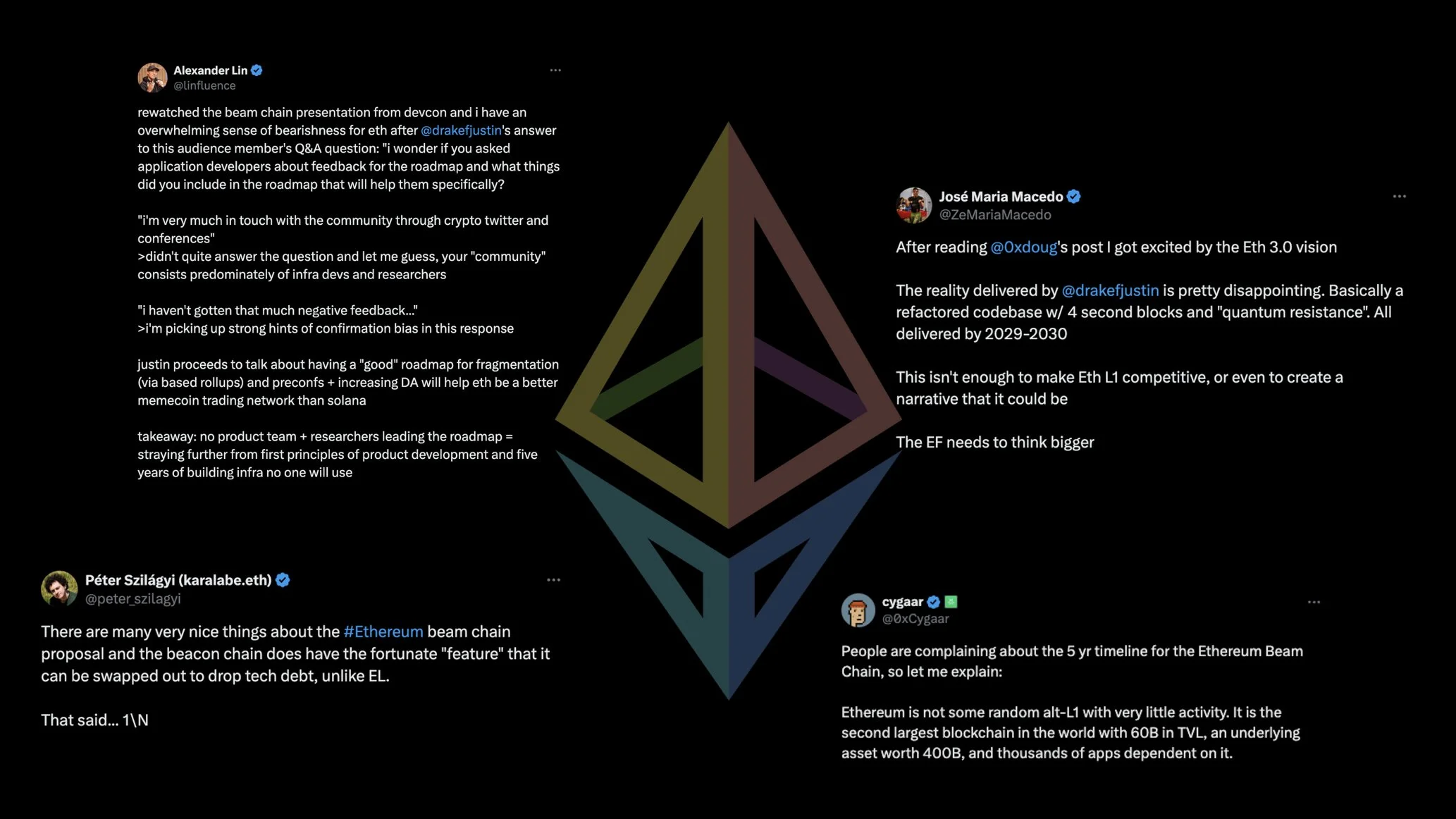
Community Reception and Criticism
The Beam Chain's extensive roadmap has elicited mixed reactions within the Ethereum community. Some stakeholders express concerns that the prolonged timeline could impede Ethereum's competitiveness, especially as rival platforms continue to evolve. Critics argue that the Ethereum Foundation should adopt a more ambitious approach to expedite these critical upgrades.
Conversely, proponents contend that the complexity and scale of the proposed changes necessitate a cautious and deliberate strategy. They emphasise that ensuring the security and stability of a network as substantial as Ethereum requires meticulous planning and thorough testing to prevent potential vulnerabilities.
Overall
The Beam Chain proposal represents a visionary yet contentious plan to advance Ethereum's consensus layer. By addressing areas such as block production, staking, and cryptography, it aspires to enhance the network and return the technical advantage over rivaling blockchain platforms. However, the success of this initiative hinges on achieving community consensus and effectively balancing the innovation with the network integrity.
We are keen on watching developments surrounding Ethereum's development and would love to support teams working in this area. If you are building something interesting, feel free to reach out to DWF Ventures.

- Details
A new report “Orange Man, Orange Coin” prepared by DWF Labs sheds light on key developments in the crypto market throughout November 2024 via data analysis, underlining stablecoin growth, DeFi expansion, and Bitcoin price records.
Summary
The crypto market has showcased clear sectoral trends, balancing institutional adoption with vibrant retail participation. Growth in stablecoins and DeFi underlines increasing maturity and potential regulatory shifts. Keeping track of metrics like Total Value Locked (TVL) and sectoral performance will be crucial in navigating the evolving market landscape.
Key Highlights
Bitcoin's Bullish Trajectory
- Bitcoin (BTC) surged to new all-time highs, nearing the $100,000 mark following Trump's election victory. This rally was supported by strong momentum across short-term, medium-term, and long-term exponential moving averages (EMAs), signaling a healthy and bullish market structure.
- The return of the “Coinbase premium”, where BTC trades higher on Coinbase than Binance, indicates renewed institutional interest. Monitoring these trends offers valuable insights into potential market shifts.
Stablecoins and DeFi on the Rise
- Stablecoin adoption, particularly USDT and USDC, continues to grow, enhancing overall crypto liquidity. DeFi also saw sector-wide outperformance, driven by speculation around deregulation and innovations like Trump's stablecoin, World Liberty Finance.
- These developments reflect broader acceptance of cryptocurrencies and their integration into global finance.
Memecoins' Resilience
- Memecoins remain a preferred speculative asset among retail investors, outperforming other sectors in terms of returns. Despite their volatility, this trend highlights ongoing retail interest in high-risk, high-reward assets.
Read the full report below.

- Details
DevCon has successfully concluded, leaving the crypto community buzzing with updates and insights. Here’s a breakdown of the most notable takeaways from the event.
Market Outlook: Optimism Amidst Bullish Trends
The recent U.S. presidential election result, with Trump securing victory, has significantly boosted confidence in the crypto market. His pro-crypto and tax-friendly stance has set a positive tone for the industry. As of November 18, 2024, Bitcoin (BTC) reached a new all-time high (ATH) near $90,000, with many anticipating it will cross the $100,000 mark soon. Ethereum (ETH), after months of skepticism from crypto Twitter (CT), rebounded strongly, surpassing $3,000. Similarly, Solana demonstrated renewed investor interest, climbing past the $200 threshold.
Strategic Moves for Project Positioning
Crypto projects launching tokens in the post-election period are experiencing robust price discovery, supported by favourable macroeconomic conditions and Bitcoin’s strong performance. As a result, many teams are targeting Q4 2024 and Q1 2025 for token listings. The current market conditions have also spurred a wave of fundraising activities, with projects viewing this as an opportune time to secure capital.
Traditionally an Ethereum-focused event, DevCon 2024 saw increased participation from non-Ethereum ecosystems such as Sui Network, Solana, Monad, and Berachain, reflecting the growing importance of multi-chain development.
Altcoins vs Memecoins: A Liquidity Competition
Altcoins are facing heightened competition for liquidity, not only from other cryptocurrencies but also from the rapidly growing memecoin sector. This cycle has proven to be more community-driven than previous ones, as evidenced by the proliferation of memecoins. While project altcoins and memecoins are often categorised differently, they are both competing intensely for retail trading liquidity.
Crypto in Bangkok: A Thriving Hub
Ethereum’s choice to host DevCon in Bangkok highlights its increasing focus on the Southeast Asian market, a region with significant crypto potential. The city’s crypto-friendly environment was evident, with Binance Thailand ads and imToken booths prominently displayed at metro stations. Attendees appreciated Bangkok’s vibrant food scene but were less enthusiastic about the city’s traffic, which led to the trending “motorbike selfie” culture on CT.
Emerging Narratives
Decentralised Science (DeSci) emerged as a key narrative during the event, drawing significant attention due to the involvement of the former Binance head Changpeng Zhao and Ethereum creator Vitalik Buterin during the Binance Labs’ DeSci Day. Additionally, Brian Armstrong of Coinbase made waves with the launch of his DeSci venture, ResearchHub.
Discussions around AI agents also took centre stage, focusing on how these technologies can revolutionise crypto user experiences. The ongoing bull market has reignited interest in decentralised finance (DeFi), with trading activities expected to surge. Conversations emphasised the need for preconfirmations and Maximal Extractable Value (MEV) improvements to enhance the sector. Meanwhile, memecoins continued to dominate trading volumes and CEX listings, showcasing their enduring popularity.
Ethereum’s New Proposal: Beam Chain
One of the most notable announcements during DevCon was the Beam Chain proposal by the researcher Justin Drake. Designed to replace Ethereum’s Beacon Chain by 2029, Beam Chain consolidates critical upgrades to Ethereum’s consensus layer, including native zk-proof support, faster transaction finality, and support for smaller validators. Justin emphasised that this proposal should not be referred to as “Ethereum 3.0.” Importantly, the Beam Chain proposal does not alter Ethereum’s broader roadmap but aims to enhance its scalability and efficiency in the long term.
Overall
From bullish moods and ATHs to new narratives like DeSci, AI agents, and the rise of memecoins, DevCon 2024 offered a clear glimpse into the future of blockchain, while the crypto-friendly atmosphere added vibrancy to the discussions. As the market continues to recover, new Web3 projects are poised to leverage the bullish sentiment, driving innovation, fundraising, and adoption across the industry. With these insights, the community is well-prepared for a promising year ahead. If you want to collaborate, you can contact the team of DWF Ventures directly.

- Details
With the election of the most crypto-friendly president to date in the United States and the continuation of rate cuts, the crypto community is abuzz with optimism. Could these changes herald the start of a new bull crypto market? Here’s a closer look at the 5 major economic adjustments and policy shifts that could become potential drivers for a new bullrun on the crypto market.
1. Fed Rate Cut and Quantitative Easing: Fueling Liquidity
Following this month’s Federal Open Market Committee (FOMC) meeting, market sentiment is optimistic for continued rate cuts in December, with a strong, over 65% probability of an additional 25 basis points cut. Such moves would signal a gradual shift in the Federal Reserve’s stance towards a more accommodative policy, possibly foreshadowing a full pivot in the coming months.
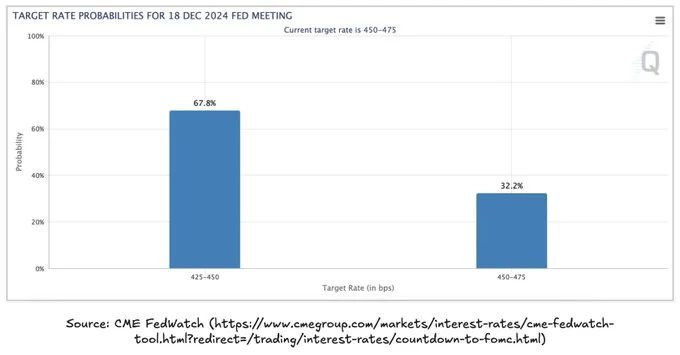
Meanwhile, China’s People’s Bank (PBC) has already announced its largest stimulus package since the pandemic, injecting liquidity and confidence into the economy. If the Fed follows suit, it would contribute to a global easing cycle that could significantly enhance market liquidity. Together, these cuts and stimuli would expand liquidity, potentially paving the way for a new bull cycle across various asset classes, including cryptocurrencies.
2. Changed Political Landscape: Regulatory Revolution for Crypto?
The recent U.S. election has brought the most pro-crypto candidates yet to Congress, alongside a crypto-friendly president Donald Trump: data from Coinbase’s Stand With Crypto initiative indicates that 247 pro-crypto candidates won seats in the House of Representatives.
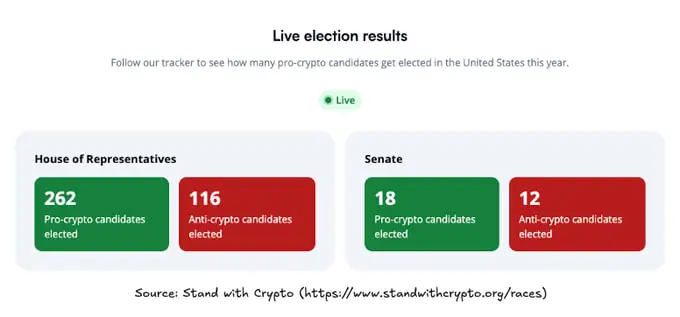
Along with high chances for the Fed rate cut, this combination creates an unprecedented opportunity for regulatory reform on the crypto market, with several critical areas that could see positive change:
- Clearer regulation for digital assets;
- New legal status for Bitcoin and its possible use by the government;
- Advancement of crypto-based ETFs;
- Enhanced support for innovations in DeFi;
Bitcoin as a Strategic Reserve
Earlier this year, Trump endorsed the idea of including Bitcoin as a national strategic reserve asset. Shortly after, Senator Cynthia Lummis introduced legislation, known as the “Bitcoin Act,” proposing to add Bitcoin to the U.S. government’s official reserve assets.
Though the act is yet to pass, it represents a substantial step toward the legitimacy of Bitcoin as a national asset. If successful, it could increase public confidence in Bitcoin and elevate crypto assets as an integral part of financial strategy. The move could also serve as a precedent for other nations, reinforcing Bitcoin’s position as a store of value and hedging asset on a global scale.
FIT 21: New Regulatory Framework
The election of a pro-crypto Congress could significantly influence the passing of the Financial Innovation and Technology for the 21st Century Act (FIT 21). This act aims to clarify the regulatory landscape by distinguishing between digital commodities and securities, a decision that could directly impact ongoing SEC investigations, such as the case involving Uniswap.
A favourable outcome for FIT 21 would provide the legal basis for DeFi protocols to implement fee switches and other governance features without fear of regulatory backlash. This would enable projects like Ethena’s ENA, which already has a fee-switch proposal, to explore new monetisation avenues, thereby fostering growth and innovation in the space. The market seems to be responding positively, with major DeFi protocols experiencing upward price momentum.
This progress could trickle down to smaller DeFi projects, potentially triggering a resurgence of the sector as a whole in the coming months.
ETFs: Emerging Opportunity for Solana
Trump’s election has already spurred renewed demand for Bitcoin, as evidenced by ETF activity reaching a record daily trading volume of $4.1 billion amid the presidential election outcome, with $1 billion transacted in less than 20 minutes. Following the successful launch of Ethereum ETFs in July, attention is turning toward other prominent assets, with asset managers already filing for a Solana ETF.
The introduction of a Solana ETF could provide substantial tailwinds for the SOL coin and its ecosystem, particularly for Solana-based projects and tokens. The ETF would further solidify Solana’s position as a major blockchain network and could drive increased institutional interest in the asset.
This shift may also affect the long-term performance of SOL relative to ETH. With Ethereum gradually losing its regulatory edge as competitors like Solana emerge, institutional investors may view SOL as an alternative with potentially higher upside, particularly as it continues to position itself as the “original ETH killer.”
Overall
The combination of a pro-crypto U.S. president, potential rate cuts, and a favourable regulatory landscape presents a promising backdrop for a new crypto bull market. With heightened liquidity from economic easing and supportive political momentum, opportunities for regulatory reform and market expansion in digital assets are on the rise. From Bitcoin’s potential as a strategic reserve asset to advances in DeFi and new ETFs for assets like Solana, these developments could not only bolster confidence but also pave the way for significant growth in the crypto ecosystem, drawing in both institutional and retail interest.

- Details
The TON Gateway 2024 conference in Dubai has concluded, and lots of insights and developments were shared by the audience. Over two days, attendees explored a wealth of information on the future of the TON blockchain, its evolving ecosystem, and new directions that extend beyond the Tap-to-Earn niche. Let’s dive into the key takeaways.
Vibes
TON Gateway has witnessed impressive growth since its debut in 2022: what began with just 150 participants has expanded to over 1,500 attendees, reflecting the rapid adoption and positive sentiment surrounding the TON ecosystem.
The event underscored a surge in developer engagement. To support blockchain developers, the TON Studio is set to launch, offering an all-in-one platform designed to facilitate the building, testing, and scaling of applications on TON.
The overall vision is for TON to become the blockchain of choice for mass adoption, focusing on mini apps, decentralised finance (DeFi), seamless payments, and user experience (UX) advancements.

The Future of Telegram Mini Apps: Not Only Tapping
TON’s recent popularity can largely be attributed to its pioneering Telegram mini apps, such as Notcoin, Hamster Kombat, and Catizen, which have effectively introduced a new sector in the blockchain industry: Tap-to-Earn.

By encouraging simple user engagement, these mini apps act as entry points for newcomers into the TON ecosystem. According to data presented at the conference, over 10% of users who try mini apps also explore other TON-based applications, a promising indicator of the ecosystem's appeal.
The financial outcome of mini apps has also been impressive. For instance, Telegram Stars generated $52 million in revenue in just four months, underscoring the demand and engagement potential:
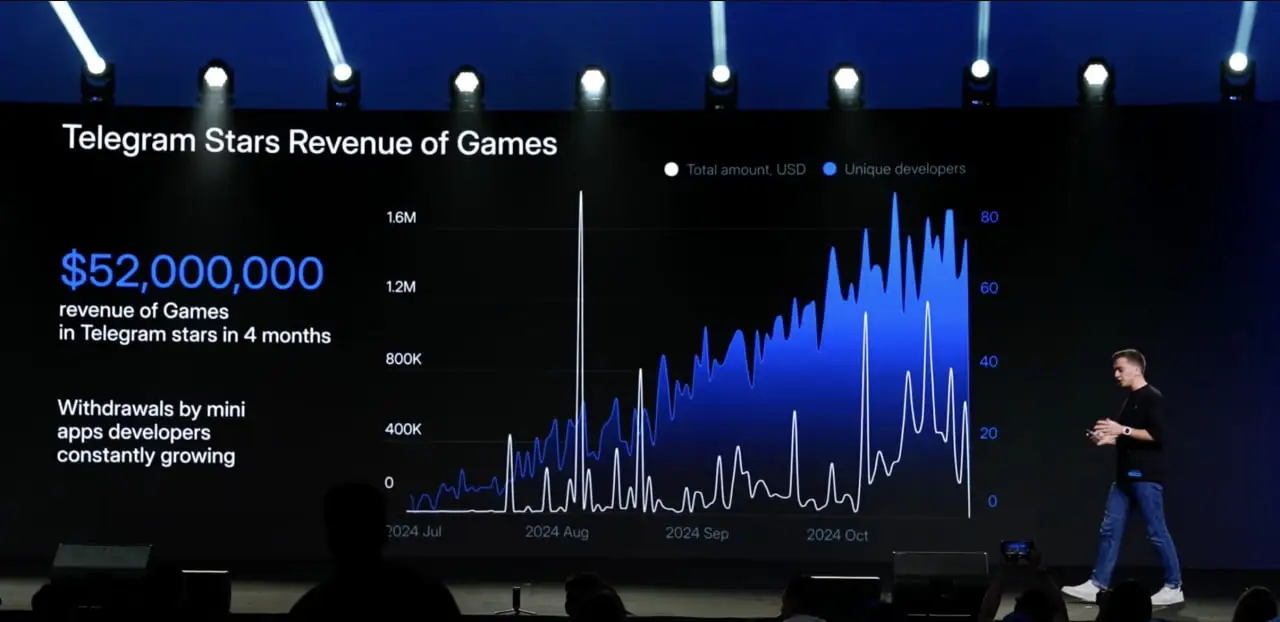
Looking forward, mini apps will likely continue to be a key acquisition strategy, but TON aims to expand beyond Tap-to-Earn by introducing more established games with enhanced user engagement. Upcoming plans include integrating gamified DeFi elements and monetisation enhancements through in-app purchases (IAP) and ads.
Stablecoins and DeFi Expansion
Building on its current traction, the TON Foundation is pushing further into DeFi. Integrations with major oracles, including Pyth Network and Chainlink, as well as bridges (LayerZero and Axelar Network), are set to accelerate this initiative. Partnerships with prominent DeFi protocols like Curve aim to introduce new financial primitives and improve automated market maker (AMM) models, enhancing liquidity and user options.
A key focus of TON’s DeFi strategy is to connect to Bitcoin and bring institutional liquidity into the ecosystem. To support this, firstly, new stablecoin infrastructure is in development, including a Dirham-pegged stablecoin to be launched in partnership with Tether. This introduction is expected to provide localised stability and appeal to regional markets.
Secondly, the forthcoming TON Teleport BTC will enable seamless transfers between the Bitcoin and TON networks, a feature bolstered by incentive programs designed to attract new users to the ecosystem.
Major User Experience Advancements
Telegram’s built-in crypto wallet has been instrumental in simplifying crypto access for users, allowing them to buy, swap, and conduct transactions via credit card. However, on-chain activity has been limited. To address this, TON introduced TON Space, a non-custodial wallet that offers a more seamless, decentralised experience for users. Through TON Space, users can perform aggregated swaps, participate in staking, and earn rewards in Toncoin (TON) with just a few clicks.
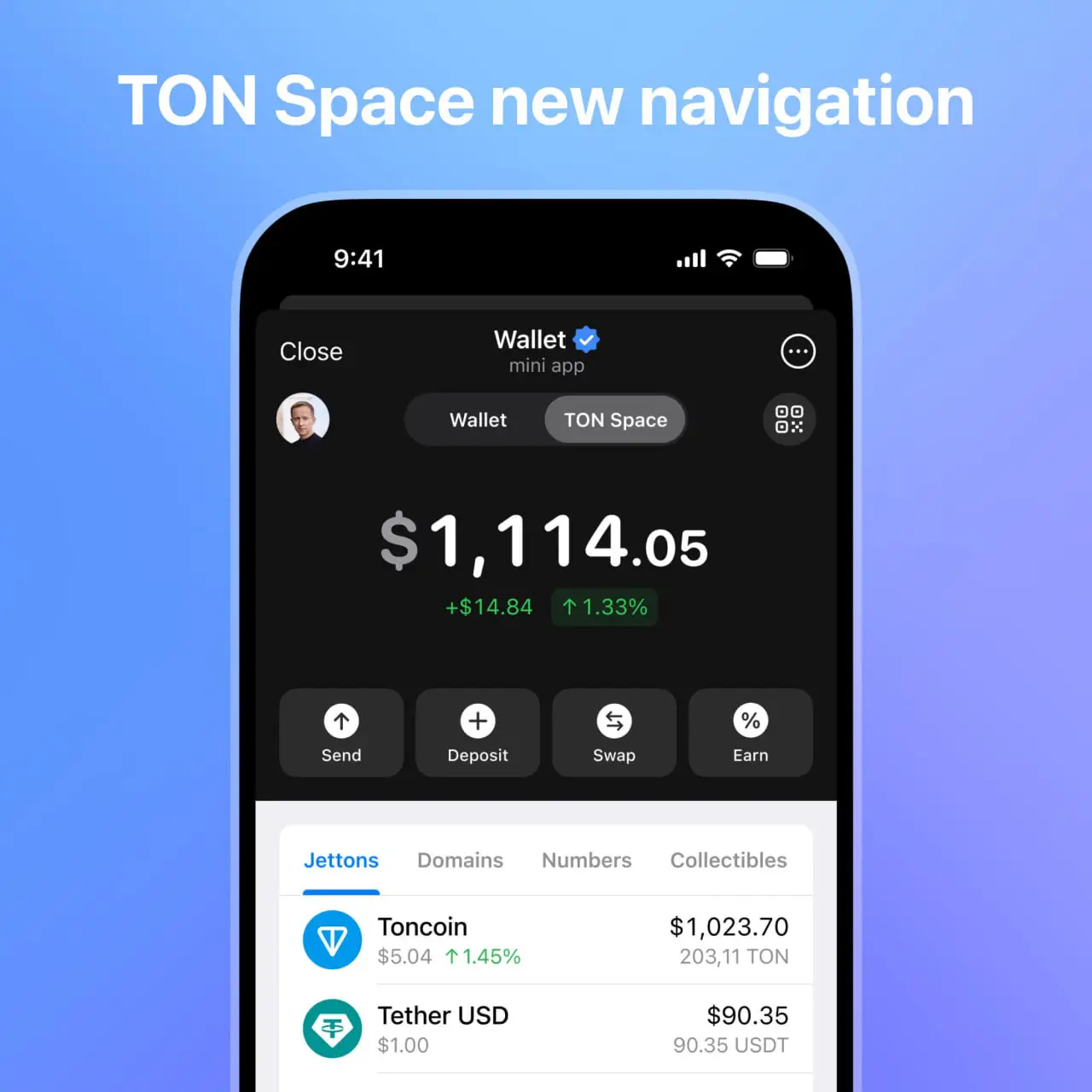
A significant advancement of TON Space is its ability to connect users directly to dapps without leaving the Telegram app, eliminating a major UX friction point and positioning Telegram as a comprehensive, user-friendly platform for blockchain interactions.
TON and DWF Labs Partnership: Building the Ecosystem Together
During the TON Gateway, DWF Labs’ Ecosystems Business Partner, Alessia Baumgartner, delivered a keynote on our company’s ongoing commitment to TON.

DWF Labs has been a key partner in supporting TON’s growth and the development of applications within its ecosystem. In 2022, DWF Labs made its initial investment of $10 million in the TON ecosystem. Further, the company has been instrumental in the growth of various projects, including Bemo, DeDust, and STON, providing both financial and developmental support to catalyse the ecosystem’s expansion. DWF Labs also joined the accelerator programme, while backing the DeFi and Data Analytics Hackathon.
Recently, the DWF Ventures team conducted an analysis of TON’s on-chain data to provide insights into the ecosystem's latest developments and future prospects. Our representatives also participated in The Open Summit in Taipei in August 2024 to learn more about the trends and sentiment around this blockchain platform.
For projects building on TON, feel free to reach out to DWF Ventures.