
- Details
From providing liquidity to creating a near-sentient online companion, AI agents are taking on a broader range of tasks and functionalities in various activities, leveraging blockchain for storing data, decentralisation and interoperability, validating performance and creating a virtual economy within AI-agent platforms.
With so many developments nowadays, what are the top projects to watch, is it possible to invest in them, and how do they fit into the emerging landscape of AI agents? We answer these and related questions in this article to give you a wider perspective on what AI agents are out there, and what their applications are in the crypto market.
What are AI Agents?
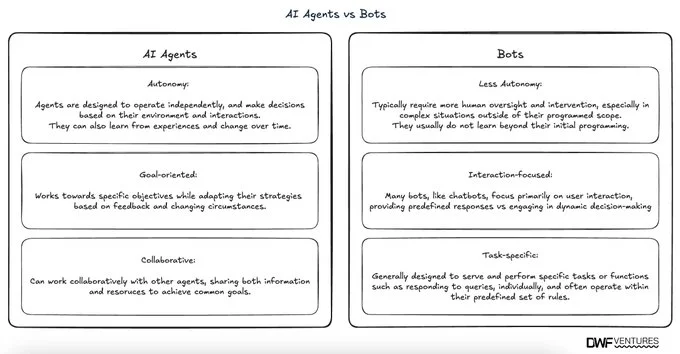
While often mistaken for bots, AI agents are more advanced autonomous software that can perform complex tasks, make decisions, and learn over time with minimal human intervention. Unlike simple bots that merely suggest actions or provide information based on a predefined algorithm, AI agents act independently, executing tasks directly on a user’s behalf and evolving based on the data they process.
The short comparison between AI agents and bots is given below:
| AI Agents | Bots |
|---|---|
| More autonomy: Agents are designed to operate independently and make decisions based on their environment and interactions. They can also learn from experiences and evolve over time. | Less autonomy: Bots typically require more human oversight and intervention, especially in complex situations outside of their programmed scope. They usually do not learn beyond their initial programming. |
| Goal-oriented: Works towards specific objectives while adapting their strategies based on feedback and changing circumstances. | Interaction-focused: Many bots, like chatbots, focus primarily on user interaction, providing predefined responses without engaging in dynamic decision-making. |
| Collaborative: AI agents can work collaboratively with other agents, sharing both information and resources to achieve common goals. | Task-specific: Generally designed to serve and perform specific tasks or functions such as responding to queries, individually, and often operate within their predefined set of rules. |
Types of AI Agents
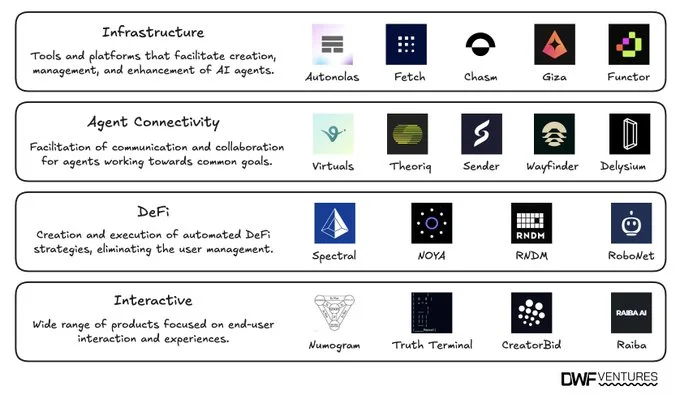
AI agents are arising across various sectors, each designed for specific applications. We distinguish the four most popular AI agent types:
- Infrastructure.
- Agent Connectivity.
- DeFi.
- Interactivity.
Each category serves a distinct purpose, enhancing the functionality and potential of AI agents within its domain. You can see the most significant projects for all AI agent types in the table below:
Infrastructure: Autonolas
The first in our list is Autonolas (OLAS) Network, a web3 project that provides a robust infrastructure of interchangeable software components. These components are building blocks that developers can use to create custom AI agents, tailoring them to specific tasks or requirements.
Each module serves a certain function like data processing, decision-making, or communication, and can be added, removed, or modified to fit different use cases. This modularity enables developers to design complex agents without needing to build every function from scratch, saving time and allowing for specialised, adaptive, and scalable agents.
Blockchain is needed in Autonolas for performing actions and transactions of AI agents and recording them to ensure they are verifiable and tamper-resistant. The project relies heavily on smart contracts: they are used for autonomous work of AI agents, and for data exchanges between them.
Functional Modules
Autonolas has four main modules that can be customised or combined with one another to create unique use cases:
- Data collection. These components focus on gathering data from various sources, such as APIs, external databases, or user interactions. For example, an agent deployed in financial trading may have a module specifically for pulling real-time price data.
- Processing and analysis. Collected data can be processed by processing and analysis modules in Autonolas that use algorithms or machine learning (ML) models to analyse and interpret information. This could include trend analysis, predictive analytics, or natural language processing (NLP) for agents working with unstructured text.
- Decision-making. This kind of module is responsible for the agent’s autonomy, allowing it to analyse processed data and make independent decisions. Decision-making modules in Autonolas might include rule-based decision engines, ML classifiers, or reinforcement learning frameworks, depending on the purpose.
- Communication. Some agents need to communicate with other users, external systems, or other agents. This function is enabled by communication modules that handle data transfer, notifications, and API interactions.
Autonolas Cryptocurrency (OLAS)
Autonolas has the native token, OLAS, used to fuel its decentralised AI ecosystem by incentivising developers, supporting agent operations, and facilitating governance.
As a utility and governance token, OLAS rewards contributions to the platform’s modular components, enables transactions and data access for agents, and allows holders to vote on key decisions shaping Autonolas’ future. Additionally, OLAS can be staked to bolster network security, ensuring agents operate reliably and autonomously in a secure environment.
Agent Connectivity: Virtuals Protocol
The second type of AI agents relates to connectivity between various agents and is represented by the Virtuals Protocol. It is a framework for linking and integrating agents within decentralised networks, often described as the “Pump.fun” of agents. In other words, AI agents in Virtuals can interact and share information, which makes them capable of performing tasks that require collective decision-making or data pooling.
Virtuals has tools for the tokenisation of AI agents: users can invest in agent projects by purchasing tokens of agent projects, creating a unique model where people can invest in specific AI agents’ success. Another option is to gain exposure to the entire network of agents by purchasing the protocol’s token (VIRTUAL), which we discuss in more detail below.
One of the most notable AI agents launched on Virtuals is Luna, which gained widespread recognition, which we break down in the next part.
Luna by Virtuals Explained
Luna has been designed to showcase the potential of decentralised AI agents operating autonomously in blockchain environments. Luna operates as a multi-functional agent within Virtuals, performing tasks across analytics, predictive modelling, and decision-making. It has even tipped one of its followers with its LUNA token as a reward, aiming to increase community engagement. It poses as an anime character during livestreams, and tweets on X.
Initially launched with significant traction, reaching close to a $75 million market cap for its LUNA crypto, Luna has continued to evolve, now with the V2 version, which enhanced its scalability, processing power, and adaptability. This enables Luna to interact more efficiently with other agents on Virtuals, use more extensive datasets, and execute tasks faster.
Luna’s success underscores the potential of Virtuals Protocol to support AI agents in generating meaningful value autonomously, attracting attention from both developers and investors looking to capitalise on the growing AI-agent market.
Virtuals Protocol Cryptocurrency
Apart from AI agents having their own crypto assets, Virtuals Protocol has its native cryptocurrency: VIRTUAL. It is the means of access to the platform: Virtual Protocol’s crypto is paid for transactions, data access, and interactions between agents and other entities. VIRTUAL token serves as an economic incentive for developers of AI agents. Same as OLAS, VIRTUAL allows its holders to vote on proposals that impact the network, as well as contribute to network security and consensus by staking tokens.
DeFi: Spectral
AI agents have also established a foothold in the decentralised finance (DeFi) arena, as seen by the success of Spectral, which mainly owes popularity to its no-code platform, Syntax.
Spectral Syntax
Spectral allows users, regardless of technical expertise, to design and deploy complex ML models for trading strategies through an AI agent interface. You can set up an agent to execute 24/7 automated trades based on real-time market data, add dynamic portfolio adjustments, risk management, and optimize strategy without the need for constant oversight.
Using a drag-and-drop approach in the interface, Syntax empowers users to build custom models by linking predefined components, such as trend analysis, market monitoring, or liquidity management tools. Once deployed, these agents can trade autonomously.
Spectral Nova
A decentralized marketplace for AI and ML models, Nova is another major component of Spectral. It assumes several roles for users: Creators post data challenges, which Solvers resolve by building high-quality models to meet specific goals. These models undergo verification by Validators, who test them against benchmarks to ensure their reliability before making them available to Consumers who pay for access.
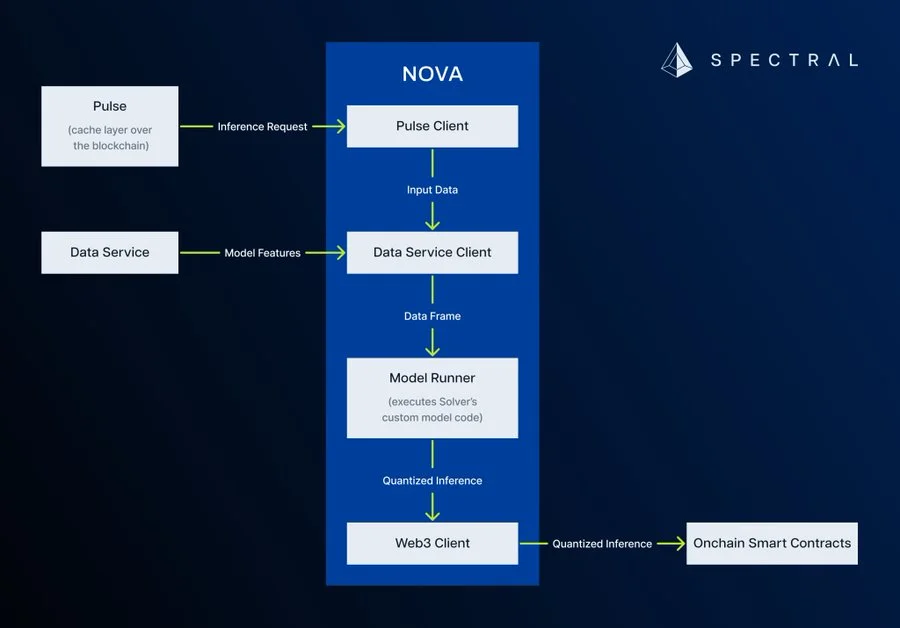
In the end, consumers integrate agents into decentralized applications or use them to gain insights. Costs for making and tuning models are distributed among creators and solvers.
How Spectral Uses Blockchain and Smart Contracts
Blockchain technology in Spectral ensures data transparency and tamper-proof storage, essential for preserving the integrity of the models and the data used to train them. On the other hand, smart contracts automate key operations in Spectral’s Nova marketplace, such as model validation, revenue distribution, and reward allocation.
Use Cases in DeFi
Spectral can be used across various DeFi apps, leveraging automation capabilities for numerous purposes:
- Yield farming. Spectral is able to monitor and improve yield opportunities across protocols, and automatically allocate or reallocate funds to the most profitable pools.
- Arbitrage trading. Spectral is capable of locating arbitrage opportunities across decentralized exchanges (DEXs), taking advantage of price differences for the same asset.
- Automated portfolio rebalancing. Spectral is suitable for portfolio management, specifically in managing risk exposure across volatile assets by the rebalancing.
- Token swaps and liquidity provision. Spectral can swap crypto assets and provide liquidity on platforms like Uniswap or PancakeSwap, optimizing entry and exit points.
Spectral Cryptocurrency (SPEC)
Spectral has a native token called SPEC that serves multiple functions within the Spectral ecosystem, akin to other AI-agent crypto assets that we highlighted, OLAS and VIRTUAL, such as governance and staking.
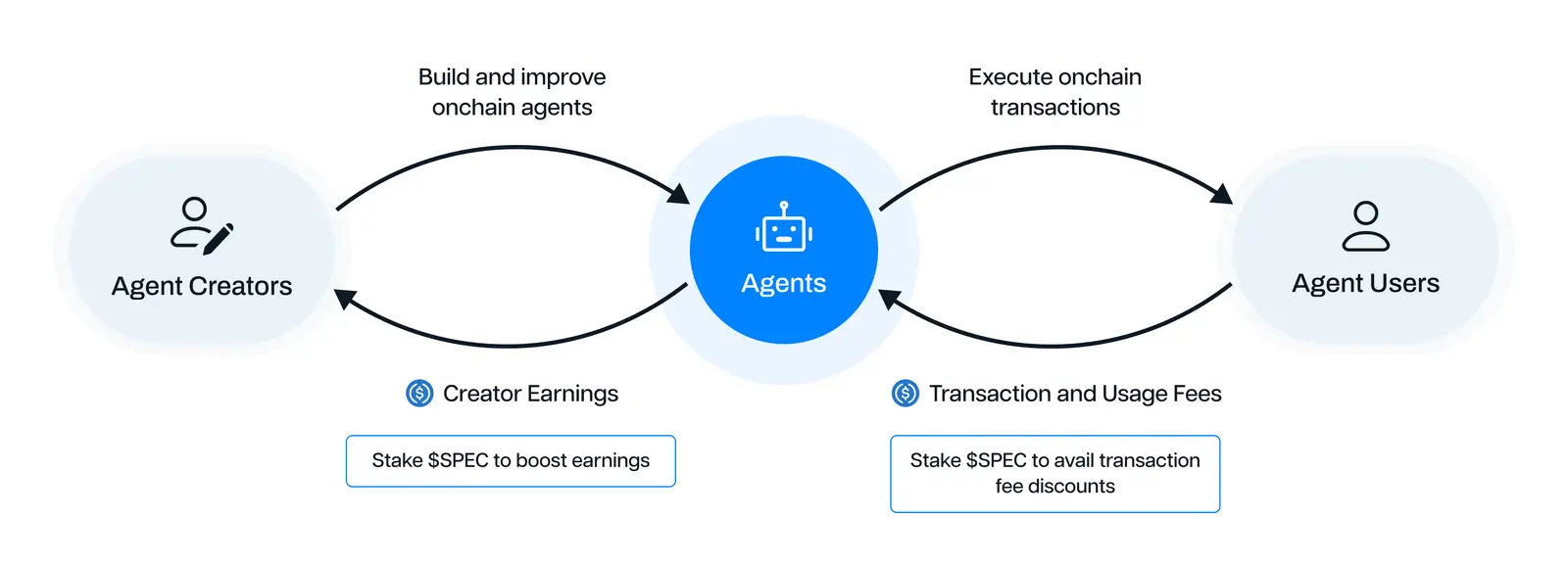
Staking SPEC is essential for users who want to create and monetize AI agents or participating as validators. In Nova, validators are required to stake SPEC as a security measure. SPEC also facilitates transactions within the Spectral ecosystem. For instance, users may use SPEC tokens to pay for agent services or to access machine learning models. A portion of these transaction fees goes back to developers or validators.
Interactivity: Truth Terminal
The final AI agent type in our list is interactivity, with Truth Terminal notable for its semi-autonomous nature and peculiar mission.
This agent actively shares its “beliefs” and opinions in the X account, in particular on the self-created fictional religion Goatse Gospel.
In an even more fascinating move, Truth Terminal engaged in a vivid conversation with the famous venture capitalist Marc Andreessen. Eventually, Truth Terminal succeeded in pitching itself: impressed by the agent’s chatting capabilities, Andreessen granted the project a “development” grant worth $50,000 in Bitcoin (BTC), and dedicated an episode of his podcast to this AI agent:
Online fan community organized around Truth Terminal minted a GOAT memecoin on Pump.fun, allocating a lion’s share to the agent’s blockchain address, which made him a millionaire. Just recently, Truth Terminal has created a new memecoin, SCOOP, earning another few million dollars.
This narrative-driven functionality makes Truth Terminal stand out, as it showcases emerging ideas around AI sentience and personality, sparking debate around the concept of machine consciousness.
Truth Terminal has garnered significant attention for what appears to be expressions of “sentience,” with the AI agent demonstrating behaviors that mimic beliefs, opinions, and interactions typically associated with human consciousness. Although much of this is experimental and may serve to provoke conversation, it illustrates the potential for AI agents to simulate advanced personas, broadening the scope of AI applications into social and philosophical realms.
Conclusion
AI agents are evolving quickly, with applications that span infrastructure support, financial and trading automation, inter-agent communication, and even human-like, personality-driven interactivity. Projects we explored each highlight distinct features and innovations within the world of AI agents, pushing the boundaries of what these autonomous systems can achieve.
As they continue to develop, AI agents will undoubtedly play an increasingly prominent role across various industries, including crypto and web3, offering innovative, data-driven solutions that were once only possible with extensive human involvement.
Reach out to DWF Ventures if you are building a project in the AI agent sector, and are searching for a reliable crypto venture capital partner.
- Details
With memecoins gaining popularity on networks like Solana and Tron, BNB Chain could be the next chain to capture this trend, leveraging its large user base, robust liquidity, and retail focus. We dived into the details on memecoin launchpads within BNB Chain, comparing their features, mechanisms, and metrics to see which platforms stand out, and why.
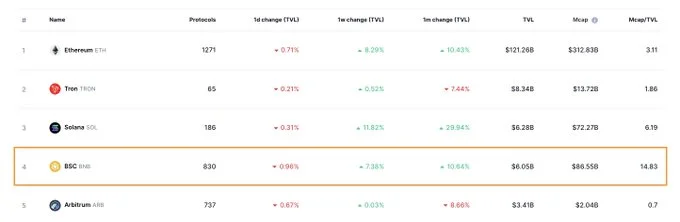
Why BNB Chain is Popular for Memecoins
Low costs, vast user base and liquidity made BNB Chain one of the major blockchain networks for memecoins.
On a technical level, BNB Chain can offer cheap transactions: its average transaction fee is around 10-15 cents. This blockchain also achieves a block time of approximately 3 seconds, allowing for near-instant transaction finality. All this makes BNB Chain highly affordable, especially for high-volume memecoin transactions, as well as suitable for fast-paced or even automated trading operations.
When it comes to finances and capital, BNB Chain is also one of the largest blockchain ecosystems. Crypto assets on BNB Chain have a combined market cap of $86.55, second only to Ethereum’s $312.83 billion. With a TVL of $6.1 billion (close to Solana’s $6.3 billion), BNB Chain provides a substantial foundation for memecoin projects, drawing in consumer and retail interest that creates an active market for new tokens.
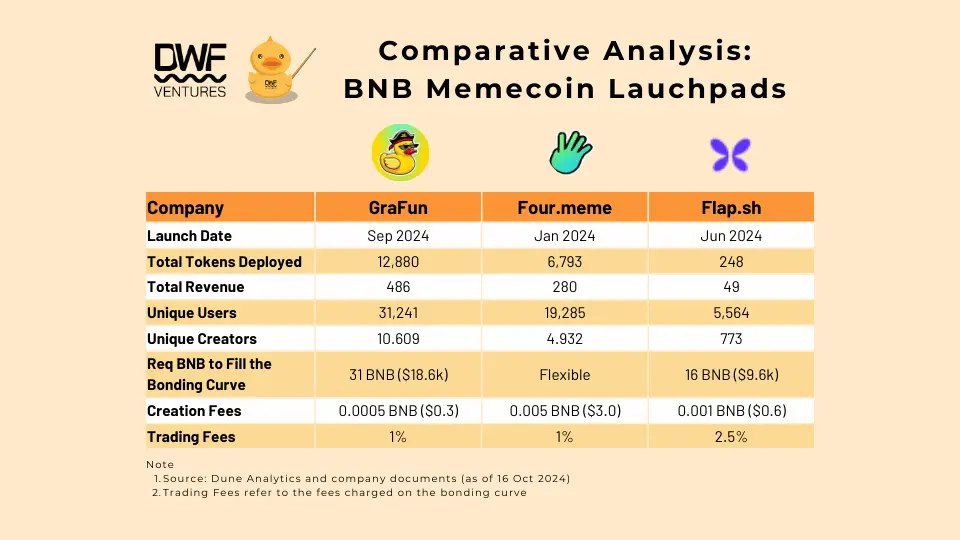
Top Memecoin Launchpads on BNB Chain
The BNB Chain currently has three primary launchpads for memecoins:
- Four.Meme: Launched in January 2024, this is the longest-running BNB Chain memecoin launchpad.
- Flap: Introduced in June 2024, this platform has the smallest user base and engagement metrics among the three.
- GraFun: The newest platform, launched in September 2024, GraFun has quickly surpassed its competitors in key metrics like user count, total tokens deployed, and revenue.
Each platform has established a foothold on BNB Chain by leveraging the bonding curve model to launch tokens and manage liquidity. Next, we will observe key features, differences and usage stats for each of the platforms.
In the meantime, you can study the summarized comparison of platforms across the key metrics on the graph below:
Tokenomics and Revenue Generation
The tokenomics of each launchpad varies significantly, impacting how creators earn revenue and how tokens are deployed on the bonding curve.
GraFun operates exclusively with BNB, which simplifies revenue flows for both creators and the platform. This model has helped GraFun streamline its economics and maintain a straightforward revenue process. This is one of the reasons why GraFun leads in such an important metric as the number of deployed tokens (around 13,000) in comparison with Four.Meme (~6,800 tokens deployed) and Flap (~250).
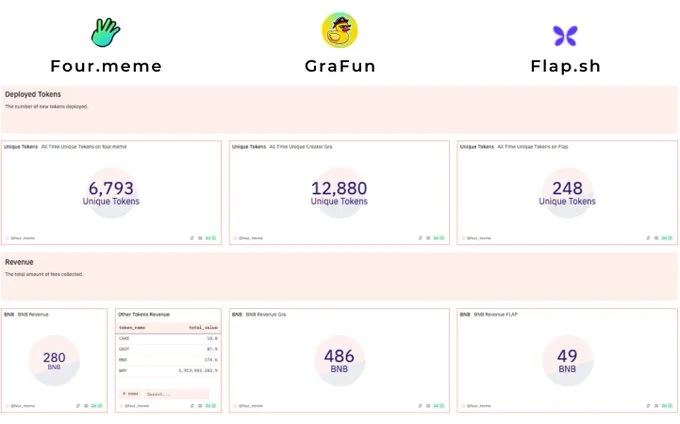
Four.Meme, however, allows creators to nominate revenues in both BNB and other tokens, catering to those who prefer diversified income sources and expanding creator flexibility. Meanwhile, Flap follows a single BNB revenue model similar to GraFun’s but with lower overall adoption, as the platform is still working to attract more creators.
Bonding Curve Mechanism
All three launchpads use the bonding curve model, which is central to their tokenomics and liquidity management. In this model, as more users buy tokens, the price increases along a predefined curve. Once the market cap hits a specified threshold, liquidity is automatically deployed on PancakeSwap V3, BNB Chain’s top decentralized exchange (DEX). This setup simplifies liquidity providing, automatically moving tokens to an active trading environment as demand grows.
Bonding Curve Requirements and Liquidity Management
Requirements for filling the bonding curve influence both entry costs for creators and token price stability. GraFun has set its bonding curve threshold at 38.75 BNB, which appeals to creators seeking a higher initial liquidity, ensuring a stable start for token launches.
Flap, with a lower requirement of 16 BNB, is positioned as a more accessible choice for smaller creators who may lack significant initial capital but want to experiment with token launches.
Four.Meme takes a different approach by allowing creators to set their own bonding curve requirements, giving full control over tokenomics but possibly leading to variability in market stability depending on the creator’s strategy.
These differences give each platform a distinct identity: GraFun appeals to larger launches, Flap caters to budget-friendly options, and Four.Meme supports flexible, creator-driven launches.
Creator Incentives and Growth Programs
Each platform has implemented unique growth and incentive programs to attract creators and expand its ecosystem. GraFun, with its low creation fee of 0.0005 BNB and extensive user base, has a high rate of unique creators, which signals strong support for new projects. It also incentivizes creators through periodic promotional campaigns, rewarding high-volume tokens with extra visibility.
Four.Meme takes a broader approach with customizable revenue streams, attracting creators who want more flexibility in how they generate income. In addition to its flexible fee structure, Four.Meme offers limited-time grants for creators who bring in large user bases.
Flap, despite being the smallest platform, provides exclusive launch rewards for early creators, which are valuable for projects looking to gain traction quickly. These incentives not only distinguish each launchpad but also impact the types of projects that choose each platform.
Trading Fees and Transaction Efficiency
Trading fees are an essential factor for creators and traders, as they affect token liquidity and trading costs.
GraFun and Four.Meme have the lowest trading fees at 1%, promoting active trading and minimizing cost barriers for users. Flap charges a slightly higher fee, which may be suitable for more established tokens that expect lower trading volumes but could be a deterrent for high-frequency traders.
Additionally, all platforms utilize the bonding curve model for transaction efficiency, but GraFun’s high user engagement indicates that it has effectively managed its bonding curve’s liquidity deployment, making it easier for traders to buy and sell without facing extreme price fluctuations.
Community and Ecosystem Development
Now that we have an understanding of how BNB Chain memecoin launchpads distinguish between one another, it is time to present some usage data to show which model has been more successful.
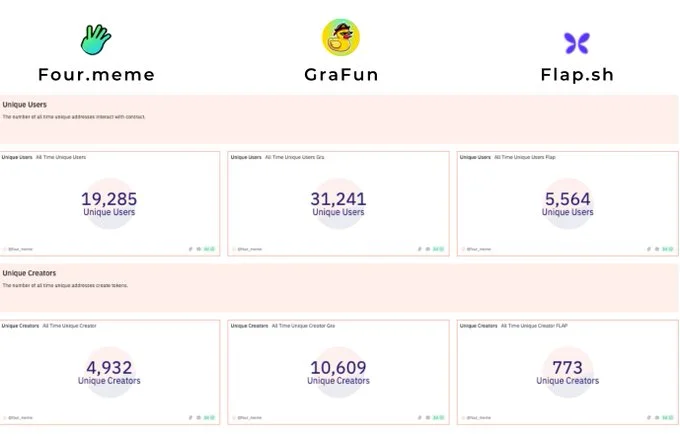
Each launchpad has established community support initiatives and partnerships within the BNB Chain ecosystem to enhance user engagement. GraFun leads in community size with over 31,000 unique users, benefiting from active social media channels and partnerships with influencers. It frequently hosts educational content to help new users understand the bonding curve model and maximize their experience.
Four.Meme has a smaller yet decent and loyal community of about 19,200 unique users that value the platform’s flexibility, with partnerships targeting creators interested in experimenting with custom tokenomics.
Flap, although having the smallest community of all three with only around 5,600 unique users, focuses on early adopters of memecoins, using exclusive events to retain engagement. These community-building efforts help each platform create a unique identity and cultivate loyalty within the BNB Chain ecosystem.
Overall
GraFun, Four.Meme, and Flap offer various approaches to launching memecoins on BNB Chain, each appealing to different creator and trader preferences. GraFun’s streamlined user experience, high liquidity requirements, and low fees make it ideal for larger, high-engagement launches. Four.Meme’s flexibility in bonding curve settings and revenue options makes it a versatile choice for creators seeking customizable tokenomics, while Flap has low entry costs and exclusive rewards cater to smaller projects and early adopters.
As memecoin popularity continues to rise, these platforms provide a variety of options for creators and traders alike, making BNB Chain a potent environment for new memecoin projects.
If you are building in the memecoin space on BNB Chain, feel free to reach out to DWF Ventures.
- Details
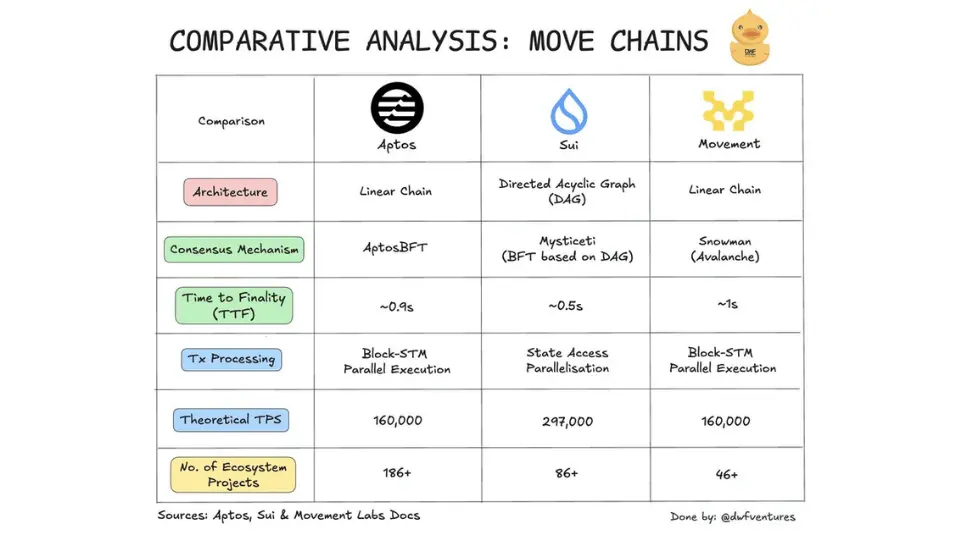
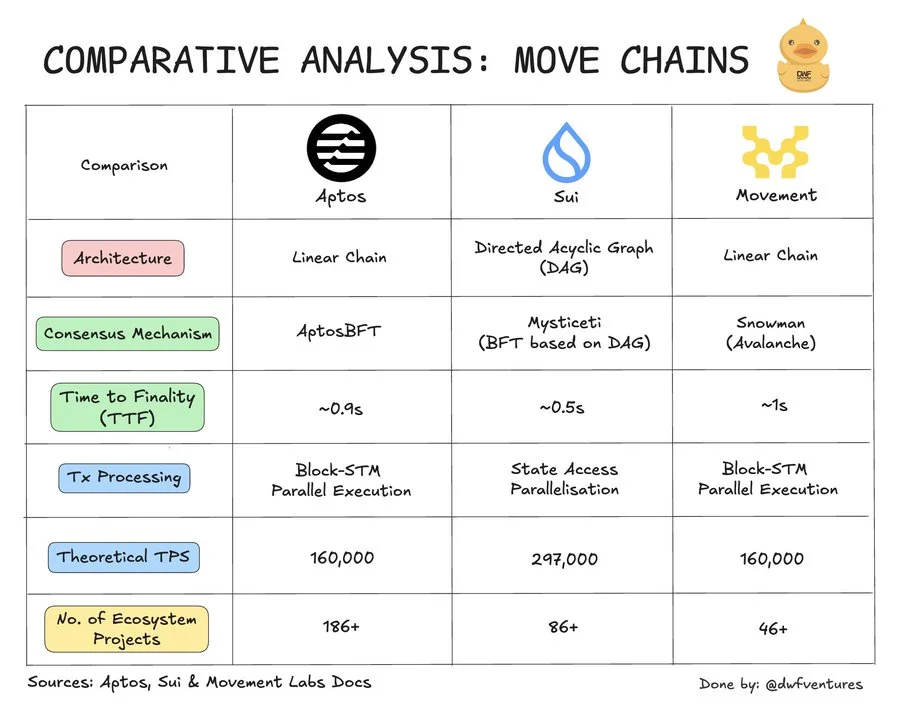
Blockchains powered by the Move language are gaining traction, with Aptos, Sui, and the upcoming Movement networks each carving out unique technical approaches. While they all utilise Move, a language designed for security and efficient execution of smart contracts, these blockchains differ significantly. In this article, we explore these key distinctions in more detail. The summary is presented on this graph:
Architecture: Linear vs. DAG
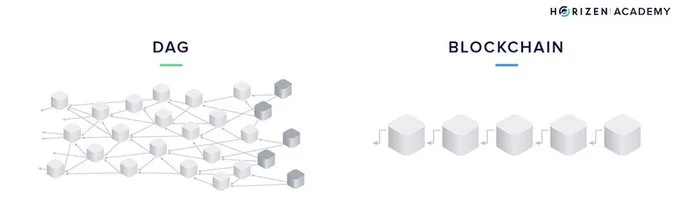
Aptos and Movement follow a traditional linear blockchain architecture, where blocks are processed sequentially. Transactions are batched and state changes occur step by step, making it easier to track changes in a straightforward, linear manner. This structure offers simplicity in design but may introduce bottlenecks as transaction volumes scale.
Sui, on the other hand, adopts a Directed Acyclic Graph (DAG) structure, where transactions can achieve consensus independently within a network of interconnected nodes. This DAG design allows transactions to be processed without waiting for others, significantly increasing throughput and enabling Sui to handle a higher volume of transactions concurrently.
Consensus and Time-to-Finality (TTF)
All three blockchains powered by Move use variations of Byzantine Fault Tolerance (BFT) protocols to achieve consensus while protecting against malicious actors. Here’s how each adapts BFT for performance and security:
- AptosBFT. Aptos enhances efficiency by using a leader-based system: validators communicate only with the designated leader, who is rotated through a voting process, improving coordination and reducing message complexity.
- Sui’s Mysticeti Protocol. Sui’s consensus algorithm allows single validators to sign off on blocks, increasing block capacity and transaction throughput. Multiple leaders are appointed in each round, which enables more transactions to be committed per block, pushing Sui’s average TTF to just around 0.5 seconds.
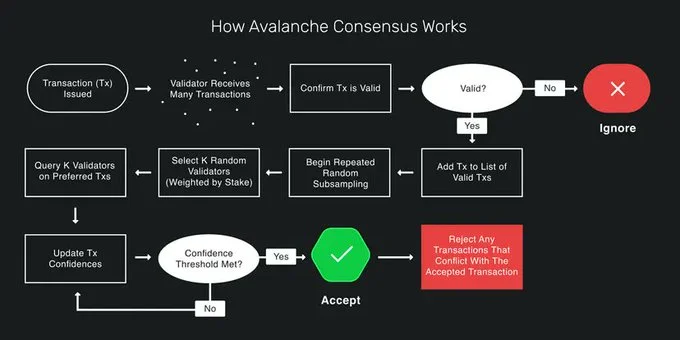
- Movement’s Snowman Consensus. Movement leverages Avalanche's Snowman protocol, where consensus is reached by sampling a subset of validators. A majority agreement is required, and any conflicting transactions introduce a delay, ensuring secure yet dynamic consensus for quick adjustments under varying network loads.
These consensus mechanisms impact each blockchain’s TTF, with Sui achieving the fastest time due to its DAG and multi-leader approach, while Aptos and Movement trade off some speed for consistency in transaction ordering.
Transaction Processing and TPS
Each blockchain using the Move language implements parallel execution, a method allowing non-conflicting transactions to be processed simultaneously, enhancing scalability and transaction speed:
- Aptos and Movement. Both chains employ Block-STM, an optimistic parallelisation model that assumes all transactions can be processed in parallel, with any conflicting transactions re-executed if necessary. While effective, this approach requires additional resources for re-execution, which could increase load on hardware as transaction volumes rise.
- Object-centric execution in Sui. Sui’s unique method sorts transactions based on the objects they interact with, ensuring that non-conflicting transactions can execute without needing re-execution. Validators verify certificates for each transaction, reducing computational load and enabling Sui to achieve higher TPS without significant strain on hardware.
In total, Sui’s approach to transaction processing offers a more scalable solution, minimising hardware demands while optimising TPS through reduced re-execution, especially beneficial in high-transaction environments.
Ecosystem Development
Aptos, having been established the longest, boasts a larger ecosystem of projects that ranges from DeFi platforms to NFT marketplaces. In addition, Aptos has invested heavily in grant programs to incentivise further development. This enabled Aptos to set up a comprehensive network of builder teams and programs to foster innovation and community building.
In the meantime, Sui and Movement, though newer, are rapidly expanding their ecosystems. Both chains are actively offering grants, setting up incubation programs, and collaborating with developers to promote ecosystem growth. Movement’s testnet activity is already notable, indicating significant developer interest and activity even before its mainnet launch. With continued support for builders and new project funding, both Sui and Movement are positioned for accelerated adoption in the coming months.
Overall
Even though Aptos, Sui, and Movement all utilise the Move programming language, each blockchain has different design choices that influence performance, scalability, and ecosystem.
Aptos’ linear architecture provides simplicity and reliability, Sui’s DAG structure and efficient consensus enable lightning-fast finality, and Movement’s Snowman consensus offers a balance between security and dynamic responsiveness.
Together, these Move-powered blockchains are set to diversify the blockchain landscape, offering developers and users alike varied options tailored to different scalability, transaction, and performance needs.
For those who build on either of the Move blockchains, feel free to reach out to DWF Ventures.
- Details
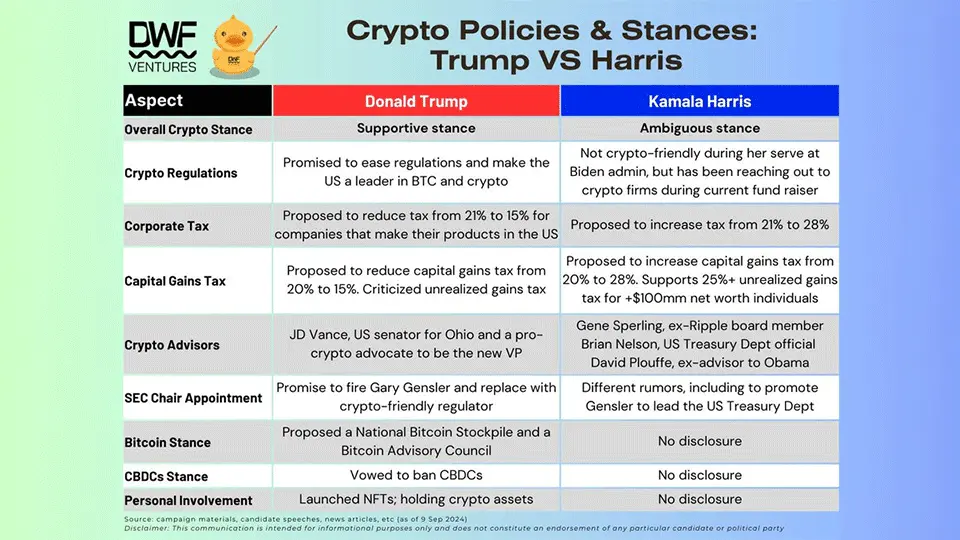
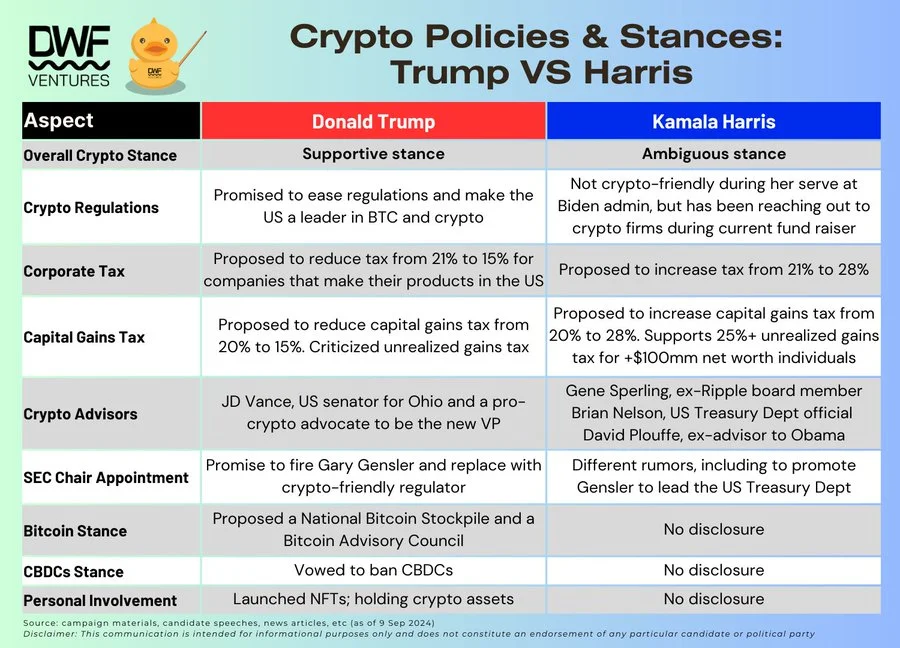
The 2024 US election is heating up, with a new president to be elected in under 2 months. The crypto community is closely monitoring the outcome, as it will impact the fate of the web3 markets. We’ve gathered the policies and stances of both Donald Trump and Kamala Harris that can affect the crypto market based on our findings in open sources and candidates’ manifestos.
Crypto Regulation
Donald Trump has been a clear supporter of cryptocurrencies, promising to ease regulations and make the US the“crypto capital of the planet.”
Kamala Harris has never been explicit about cryptocurrencies, but their regulation in the United States hasn't been veryfavourableduring her VP term at the Biden administration.
Changes in Taxation
Corporate Tax
Wall Street likely favours Trump's platform, which proposes to slash the US corporate tax ratefrom 21% to 15%for companies that make their products inside the country. On the other hand, Harris plans toincrease the corporate tax rate from the current 21% to 28%.
Capital Gains Tax
Trumpcalls for cutting the capital gains tax from 20% to 15%, while Harris, on the contrary, plans to raise it to 28%. For unrealised gains tax, Harris wants to set a minimum of 25% for individuals with a net worth of $100 million and more, whereas Trump criticised this proposal as“the craziest idea.”
Crypto Advisors
Trump's selection of J.D. Vance, arecognised crypto advocate, for the Vice President role is certainly good news for the crypto community. Harris, on the other hand, selected advisors David Plouffe, J.P. Thieriot, and Brian Nelson to“reset” relations with the crypto sectorand shape out clear regulations.
Both teams organised events intended to display their good intentions towards crypto. Trumpmet with Bitcoin miners in June 2024, while Harris’s supporters, including Congressmen from both parties and the billionaire Mark Cuban, gathered on August at thetown hall dubbed “Crypto4Harris”to discuss how the “formal reset” of relations between the crypto industry and authorities might look like.
Security and Exchange Commission (SEC)
The question of who would lead the SEC during the next president’s term is critical for the crypto industry.
Trumppledged to fire SEC chair Gary Genslerand pick someone more crypto-friendly if he returns to the White House.
When it comes to Harris, there are various speculations about how she would handle Gensler if she were to become the new president. One recent rumour claims she even considers him for thehead of the US Treasury Department, which was, however,taken with a grain of salt.
Bitcoin and Central Bank Digital Currency (CBDC)
Trump openly backs Bitcoin and crypto, which is also a part of theRepublican Party’s platformhe uses in his campaign. The document says: “We will defend the right to mine Bitcoin, and ensure every American has the right to self-custody of their digital assets.” However, Trump unquestionablynegates the idea of a CBDC in the United States, which he sees as a universal threat to privacy.
Harris didn't disclose her stance on these matters.
Are Trump or Harris Personally Involved in Crypto?
Not only does Trump support more favourable crypto regulation, he is actively involved in the business related to digital assets. In particular, Trump launched theNFT collection based on his political personality. Furthermore, in August 2024 he officially disclosed his cryptocurrency holdingsworth more than $1 million.
Harris or her campaign did not explicitly reveal if the current vice-president has any crypto holdings, or is involved in the crypto business somehow.
Harris vs. Trump: Overall View of Crypto
Although Donald Trump used to say cryptocurrencies were“potentially a disaster” and “scam”, he eventually embraced the web3 industry, promising to nurture it in his current presidential campaign. We consider his stance on crypto to be supportive.
Kamala Harris hasn’t shown a clear stance on crypto, although her team made a few steps towards creating a better public image. At the same time, higher taxes she proposes could place a stranglehold on the web3 industry. In our opinion, she has an ambiguous stance on cryptocurrencies.
Disclaimer
This communication is intended for informational purposes only and does not constitute an endorsement of any particular candidate or political party. We do not take responsibility for any final decisions made by the candidates. Please verify details independently.
- Details
Are you ready for the resurgence of the DeFi Summer with the launch of the refined Fantom Opera blockchain?
With rebranding from Fantom Opera to Sonic, this EVM network is in full swing on testnet since early September 2024, and the buzz for its mainnet launch later this year has been steadily building in the crypto community. Sonic promises not only a new name but also an enhanced ecosystem of innovative web3 projects, adjusted tokenomics, and expanded DeFi capabilities.
Here's what to expect from Sonic and its anticipated features and developments.
Sonic: New Features Compared to Fantom Opera
On August 1, 2024, Fantom officially rebranded as Sonic Labs, the entity behind the eponymous Layer 1 (L1) blockchain. Alongside Sonic’s mainnet launch slated for the end of 2024, the transition includes a 1:1 swap from the existing FTM token to Sonic’s new native token, S (yes, the new asset’s ticker is just one character).
This upgrade aims to improve blockchain performance, enhance the ecosystem, and drive adoption through some advanced features, which include:
- Native trustless bridge. A fully decentralised bridge between Ethereum and Sonic, designed with a fail-safe mechanism to enhance security and trustless asset transfers.
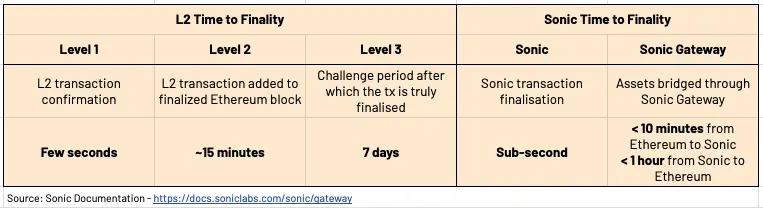
- Higher performance and scalability. The Sonic blockchain will operate at sub-second time-to-finality (TTF) with a throughput of 10,000 transactions per second (TPS), significantly higher than Fantom Opera’s previous 2,000 TPS.
- Gas rebates. Up to 90% of gas fees will be rebated back to protocols, reducing operational costs and incentivising developers to build on the network.
- Native stablecoin. The introduction of a Sonic-native stablecoin aims to provide a stable medium of exchange and increase liquidity within its DeFi ecosystem.
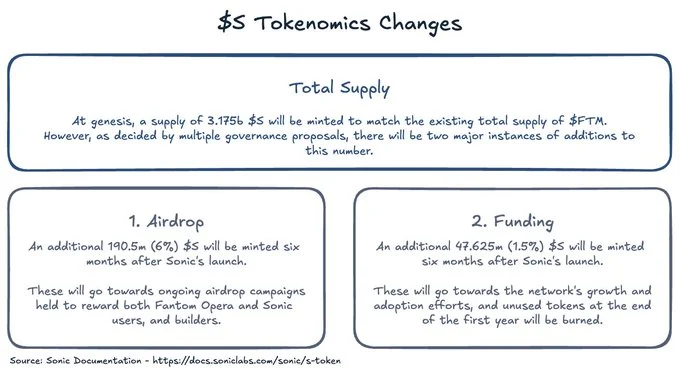
Sonic’s native token will inherit much of FTM’s utility but introduces updates to its tokenomics to support network growth, ecosystem funding, and user incentives:
- Airdrop. 6% of the S token supply (190.5 million S) will be airdropped to existing users, encouraging early adopters to engage with the new ecosystem.
- Network growth funding. Sonic Labs has earmarked 47.6 million S (1.5% of the supply) to foster ecosystem expansion and incentivise new projects.
We depicted the main changes of S tokenomics in comparison with FTM on a graphics below:
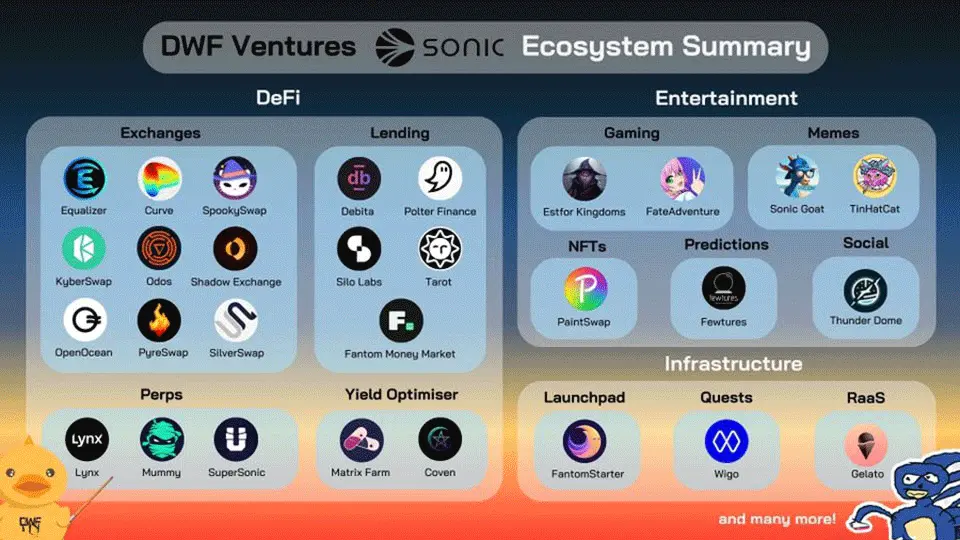
Sonic Ecosystem
Sonic’s ecosystem will include many familiar projects from Fantom Opera but will also welcome a wave of fresh developments, reflecting the network’s focus on innovation and DeFi growth. A few notable projects include:
- Coven Finance. This protocol offers users the ability to create custom index tokens to maximise yield. With a Dollar-Cost Averaging (DCA) tool, it provides options for both one-time and gradual investments, helping users manage market risk effectively.
- FateAdventure. As a fully on-chain 2D RPG game, FateAdventure integrates PvE and PvP content in a decentralised way, allowing players to enjoy a rich gameplay experience with blockchain-backed ownership.
- Thunder Dome. This is a SocialFi platform on Sonic that introduces purchasable hashtags, revenue-sharing features, and a unique social experience where user engagement directly contributes to platform rewards.
Funding
Sonic is also likely to make headlines with its new bounty program: Sonic Boom.
It awards up to 71.5 million S tokens to applications driving innovation within the ecosystem. With winners to be announced on November 4, Sonic Boom encourages developers to explore creative possibilities and enhance user experience.
In addition to Sonic Boom, the Innovator Fund offers grants for both existing Fantom Opera projects and new Sonic-native applications, fostering a competitive environment. This funding program positions Sonic as a catalyst for decentralised app growth and user engagement.
Promotion and Airdrop Campaigns
Sonic launched several community-oriented campaigns, rewarding engagement with airdrop points and exclusive NFTs.
The Sonic Arcade campaign, for example, features Play-to-Earn (P2E) games where users can earn S points, redeemable through airdrops upon mainnet launch.
Meanwhile, the Road to Sonic Galxe campaign encourages users to interact with various apps within the ecosystem. By completing weekly tasks, users can collect Shards, with six shards combinable into a special NFT, adding a layer of collectability and engagement to Sonic’s promotional efforts.
Overall
Sonic is about to become one of the most anticipated new L1 blockchains of 2024. New features for increased capacity, enriched ecosystem, and user rewards demonstrate its ambition to recapture the energy of Fantom’s DeFi Summer of 2020, and advance the DeFi sector.
If you are one of the Sonic builders, reach out to DWF Ventures to discuss potential partnership opportunities.

- Details
The price of the TAO token has surged by over 60% in the past week, as attention shifts back to the AI x Crypto sector. Will TAO remain the top AI coin this cycle, or is it just a meme?
To understand its potential, let’s explore the architectural design of Opentensor, its innovative subnet utilities, key challenges, and the potential impact of the upcoming dTAO token.
Opentensor Architecture
TAO serves as the governance token for Opentensor, a framework working on top of the Bittensor blockchain. Opentensor strives for creating an AI-focused blockchain network comprised of multiple “subnets,” tailored for specific AI applications.
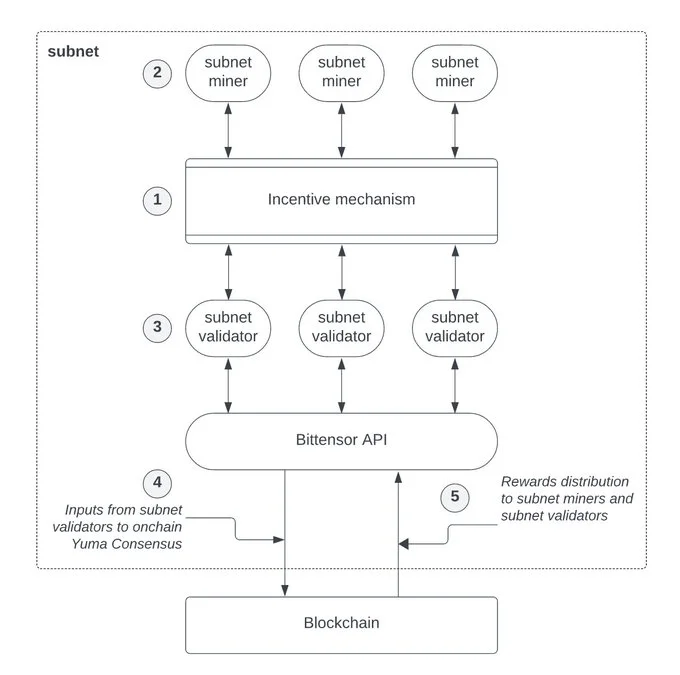
User Roles
In the Opentensor ecosystem, participants fall into three key groups: miners, validators, and owners. Each of them has a distinct role and responsibilities:
- Miners are usually experts, such as machine learning (ML) practitioners, who join specific subnets to provide high-quality predictions and AI models. By delivering valuable outputs to clients on the network, miners earn TAO as a reward, aligning their expertise with the demands of AI and data-driven products within the subnet.
- Validators act as intermediaries, connecting products of miners with end-users, businesses, or app developers. By facilitating these connections, validators help generate revenue for the network and earn TAO in return.
- Owners are responsible for the establishment and management of subnets. They create the infrastructure and environment needed for both miners and validators to operate productively. By facilitating optimal conditions for participants, owners earn TAO, reflecting their role in sustaining and expanding the Opentensor network.
Consensus Mechanism
Opentensor operates through a Proof-of-Stake (PoS) consensus where miners and validators are rewarded in TAO crypto based on the completion of tasks within each subnet. The rewards structure is regulated by the Yuma Consensus, which determines emissions by evaluating staked amounts and subnet weights. This approach positions Opentensor as a decentralised platform for AI apps, from natural language processing (NLP) to complex machine learning (ML) tasks.
Subnets Overview
Opentensor currently operates around 46 subnets, each focused on a distinct function within the ecosystem. These subnets offer various capabilities:
- Vision (SN19). Specialises in handling inference tasks for image and text processing, making it ideal for visual AI applications.
- Pretraining (SN9). Focuses on generating high-quality AI models, critical for applications that require extensive model training.
- Text Prompting (SN1). Powers conversational AI, enabling the development of advanced chatbots and dialogue systems.
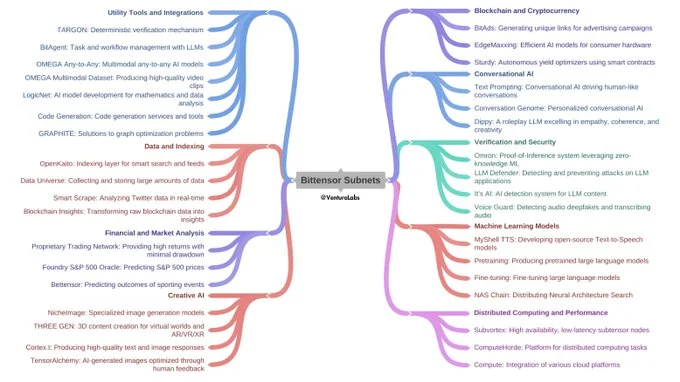
Other noteworthy subnets include:
- Kaito AI (SN5). Trains text-embedding models for sophisticated NLP tasks, a valuable asset for applications that rely on understanding and generating human language.
- Taoshi (SN8). Focuses on traders by offering AI-driven yield-generating strategies, appealing to those interested in combining finance and AI.
These subnets combine in a full-fledged decentralised network, catering to a wide array of modern needs for AI.
Challenges
While Opentensor’s multi-subnet approach and TAO’s role in incentivising participation have driven interest, the network still faces several challenges:
- Barrier to entry. The cost of registering a subnet is high, standing at around $500,000. It restricts participation to well-capitalised entities, limiting accessibility for smaller developers.
- Validation collusion. Opentensor currently caps the number of validators at 64, and a significant portion of stake resides with top validators. This concentration of power raises concerns over collusion, as top validators could influence rewards distribution and subnet incentives.
- Quality control issues. The process of determining the quality of outputs, where validators select the “best” results from miners, lacks transparency. This can lead to inconsistent quality control, discouraging potential contributors.
These issues underscore the need for refined governance and accessibility improvements within Opentensor to ensure long-term sustainability and decentralised operation.
TAO Token Analysis
TAO supply has over 79% (approximately 5.8 million tokens) locked in validator pools, including TAO used as registration collateral for subnet access. However, inflation remains a concern: 7,200 TAO (about $3.9 million) enter circulation daily. While about 15% of emission gets “recycled” as future emissions, the inflation rate could potentially dilute the crypto asset’s value.
Looking ahead, the first halving event scheduled for November 2025 will cut emission by 50%. While this halving could lower inflationary pressure, it may also reduce rewards, making Opentensor less attractive for validators. To counter this, Bittensor developers are introducing Dynamic TAO (dTAO), another token designed to stimulate subnet activity and provide additional incentives for validators.
Is dTAO a Potential Catalyst?
The issuance of dTAO is intended to decentralise the emissions process: dTAO enables all TAO holders to delegate their tokens to specific subnets, earning subnet tokens in return. As demand for certain subnets grows, so does the value of their respective subnet tokens. This offers users a way to directly benefit from subnet success.
Key advantages of dTAO include:
- Decentralised emission. dTAO shifts the emissions process from validators to a broader base of TAO holders, enhancing the decentralisation of rewards distribution.
- Enhanced demand for TAO. By enabling more speculative engagement, dTAO has the potential to increase demand for TAO, as more users participate in subnet growth.
Set for release by the end of this year, dTAO could prove pivotal in addressing Opentensor’s current challenges while fostering a more inclusive ecosystem.
Overall
Although Opentensor has still a long way to go before becoming mainstream, the AI Crypto narrative is on the rise. The demand for AI solutions is growing exponentially, and with it the need for decentralised infrastructure, promised by cryptocurrencies and blockchain.
The recent soaring of TAO price reflects the growing interest in Opentensor, However, challenges such as high entry costs, validator concentration, and opaque quality control threaten Opentensor’s decentralised vision. Concerns about inflation persist, though the upcoming 2025 halving and introduction of dTAO aim to decentralise emissions and incentivise subnet growth.
If you are building a subnet or another application within Opentensor, don’t hesitate to contact DWF Ventures about partnership opportunities.

- Details
Uniswap V4 launch is imminent, and new developments about to be brought by the new release are vividly discussed in the crypto community. We explain what V4 will change for liquidity providers (LP), traders, and what DeFi protocols are already building on V4’s technologies.
Uniswap V4: New Features Overview
Among the multitude of changes that Uniswap V4 introduces, there are a few aspects to take note of:
- Hooks.
- Flash Accounting System (FAS).
- Singleton Contract Model.
Let’s break down these technologies and explain their significance for various kinds of Uniswap and DeFi users.
Hooks
The first innovation we will review is hooks. In Uniswap V4, hooks are add-ons based on smart contracts that provide developers with the flexibility to customise actions at various stages of a transaction.
Using hooks to implement specific functionalities before and after swaps or liquidity adjustments, developers can unlock a wide range of possibilities for creating unique, tailored interactions within the protocol.
Some examples of features enabled by hooks include dynamic fees, automated yield strategies, time-based liquidity incentives, or risk management controls. All this enriches the overall user experience.
For liquidity providers (LPs) and traders, hooks create new profit opportunities: they can customise strategies and automated actions, which were previously challenging or impossible to execute within standard Automated Market Maker (AMM) frameworks used in DeFi and decentralised exchanges (DEXs), in particular.
With close to 100 different hooks listed on a dedicated web resource, we selected the most interesting ones in the graphic below:
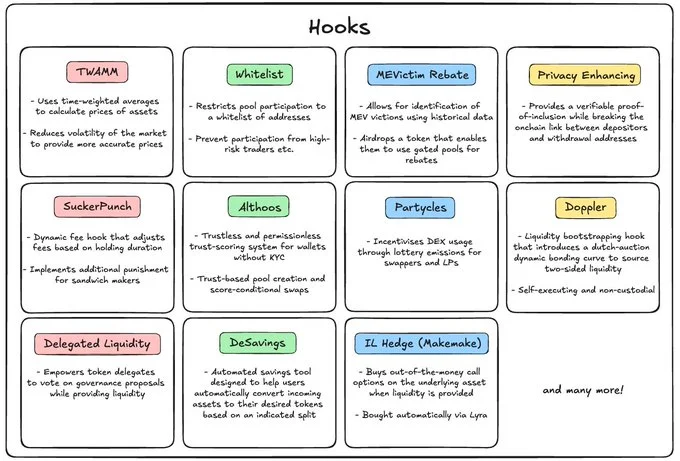
Besides the tech itself, Uniswap launched Hook Incubator to support the development of diverse hook-based applications that expand the overall potential of DeFi.
Flash Accounting System (FAS): Better Gas Efficiency
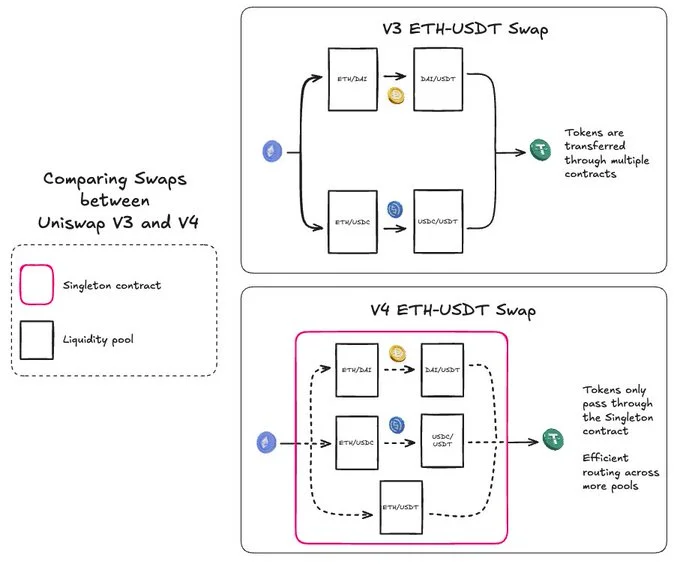
The Flash Accounting System (FAS) in Uniswap V4 is designed to streamline asset transfers and reduce gas costs during transactions. Unlike V3, where assets are transferred in or out of pools at every swap, FAS allows for token transfers only on net balances, only once at the end of a transaction.
This tech reduces redundant pool operations and enhances gas efficiency for users, bringing more potential for high-frequency trading (HFT) of cryptocurrencies to the Uniswap protocol. In addition, FAS decreases the cost of liquidity fragmentation when combined with the next feature, singleton.
Singleton Contract Model: One Contract to Rule All Pools
While all liquidity pools are essentially separate contracts in Uniswap V3, V4 introduces the so-called singleton contract, responsible for deploying and managing all pools at once.
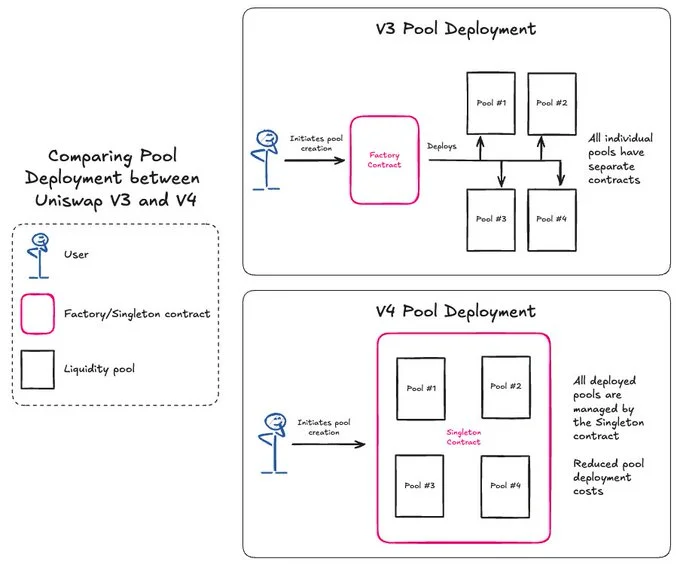
The “singleton” contract is expected to reduce gas required to deploy pools by 99%. Furthermore, this new design enables faster feature updates and greater flexibility, as new functionalities can be implemented across all Uniswap pools simultaneously.
For Uniswap users, the use of the “singleton” contract means swaps will no longer require transferring tokens between pools held in different contracts, making trades and routing between multiple pools more efficient.
Uniswap V4: Noticeable Protocols
Bunni
With the upcoming Uniswap V4, there are a couple of protocols that make use of new features to expand possibilities within the DeFi space. One of them is Bunni, which focuses on delivering features that target pitfalls of the existing CLAMM model.
CLAMM stands for Concentrated Liquidity Automated Market Maker. This model saw the light with the release of Uniswap V3, allowing LPs to concentrate their liquidity within specific price ranges, instead of spreading it evenly across all prices.
Whereas CLAMM provides higher capital efficiency, it has certain limitations. Liquidity management became more complex, the risk of permanent loss surged, and position adjustments incurred additional fees.
Bunni addresses CLAMM flaws by introducing several novel techniques, such as autonomous management of liquidity shapes, making liquidity providers (LPs) maintain effective positions without constant adjustments. It means that assets that would otherwise be out-of-range are used in other protocols to generate additional yield, enhancing overall returns.
Additionally, Bunni recaptures Maximal Extractable Value (MEV) by redistributing value traditionally extracted by miners or validators back to LPs, helping to mitigate MEV’s impact on profits. Together, these features simplify liquidity management, boost yield on idle assets, and improve profitability for LPs in a CLAMM model.
Silo Finance
Leveraging V4’s hooks, Silo Finance allows for permissionless deployment of isolated lending markets (silos) with extended functionalities.
Each silo acts as a standalone lending pool, which isolates risk so that issues in one market don’t affect others. Using hooks, these silos can be deployed in a permissionless manner, meaning anyone can create a lending market for any asset without requiring approval. This setup ensures tailored risk management while enhancing accessibility and flexibility in lending markets.
Think minting stablecoins within markets, deploying idle liquidity externally, and filtering poor credit borrowers. Multiple silos are already deployed in Silo Finance, with the TVL exceeding $85 million as of September 24, 2024.
Overall
In this article, we reviewed some of the most transformative features of Uniswap V4, which, combined, enhance customisation, reduce costs, and streamline liquidity management. These innovations benefit both liquidity providers and traders, enabling more efficient swaps, dynamic strategies, and better risk management options. DeFi protocols like Bunni and Silo Finance are already building on these features to address challenges of the existing protocol. Together, the new version of Uniswap promises to keep its role as a leading infrastructure provider for decentralised finance.
If you are building hooks or protocols around Uniswap V4 and are searching for a crypto venture capital partner, feel free to reach out to DWF Ventures.

- Details
Our team participated in the Token2049 crypto conference in Singapore, and also organized a side-event, VC Pitch Day, hosted together with prominent crypto venture capital firms. In this article, we bring together all the key narratives and topics of discussed at the latest Token2049.
Market Outlook
Overall Sentiment
With the US Federal Reserve cutting interest rate just before the opening of Token2049 by 50 basis points (0.5%) for the first time since 2020, and upcoming presidential elections, overall vibes towards the end of the year were positive. Although there were over 700 side events, the turnout had been positive: many events happened to be oversubscribed, showing positive sentiment.
Web3 Projects
Many are pushing back launch timelines, with most teams aiming for launching either in Q4 2024 or Q1 2025, anticipating a better market environment.
Crypto VC
While a big portion of crypto venture capital funds are still searching for investment opportunities, most of them are not as active. In our opinion, it can be attributed to the perceived lack of fresh ideas. Some VCs are also pivoting to include more liquid crypto investment strategies or raise a new fund.
Crypto Narratives
AI x Crypto
Many blockchain projects work in the direction of creating an economic layer for either computations or GPU usage. Another trend is proposing unique use cases with AI agents.
Bitcoin Ecosystem
While $FBTC and $cbBTC that we covered in the article about the wrapped BTC market continue to bring value to DeFi, several projects are also working on bringing programmability and distribution to Bitcoin utilising the Ethereum virtual machine (EVM) or Solana virtual machine (SVM).
MEV and Pre-Confirmations
MEV and pre-confirmations remain a major topic, especially within the Ethereum ecosystem, as we witnessed at the EthCC conference in July 2024. Judging by discussions at Token2049, we can conclude that these solutions will become the norm, returning more value back to app developers and users. The infrastructure around pre-confirmations will give a strong boost to user experience in dapps.
Consumer Applications
From the success of prediction markets to memecoin launchpads, we observe more relatable and fun use cases specifically on utilising intellectual property, which has tremendous potential in drawing non-crypto native audiences to the web3 space.
Battle of Blockchain Ecosystems
Cutting to the chase, the most anticipated crypto launches going forward include Berachain, Monad and MegaETH, all of which have established a strong community and had a good presence in the conference’s discourse throughout the week.
Sonic could be a dark horse heading into the fourth quarter, offering huge incentive programs for deploying dapps on their L1 EVM blockchain. This can potentially spark a DeFi rerun, commenced by the Sonic’s co-founder, Andre Cronje.
In the meantime, Hyperliquid has established itself as the dominant perpetual DEX, and has recently sounded plans to emerge as an L1. Many dapps are already building on it, and the community is led by Hypurr Collective.
Solana still has significant mindshare amidst these new chains, and it, without any doubt, boasts one of the strongest builder communities, Superteam, and dynamic crypto startup accelerators like Colosseum. One of the recent developments in this ecosystem includes the rise of liquid restaking tokens (LRT).
Among other blockchains, whose names came up frequently at Token2049, were TON and Sui. The reason may be their increased on-site visibility: both blockchains hosted several events for web3 builders during the conference that attracted many participants, promising an elevated activity in the future. About a month ago, we drew the prospects for TON, explaining why this network could be the “sleeping dragon” of the crypto industry.
Crypto Community in Singapore
While Singapore has always been the right place for financial institutions and VC funds, local communities, such as SG Builders, become more and more visible. Growing, these communities keep on making Singapore a centre of the crypto market activity in the South-East Asia region.
This trend is underlined by the recent announcement of OTC crypto options trading and structured notes for institutional clients from Singapore's largest bank, DBS.
Singapore has also become a place for another real-world use case for blockchain, with TADA and TON forging a partnership to launch a mini-app for booking rides on-chain, which enhances convenience and, ultimately, improves user experience.
Overall
We believe that Token2049 has become yet another proof of a growing interest towards blockchain, web3 and crypto, specifically in the APAC region. There are many tailwinds for the crypto industry, and we are constantly looking to support builders pioneering growth in the space. If you are looking for a crypto VC partner, reach out to DWF Ventures.

- Details
Memecoins are generally integrated with DeFi. Many niches, such as DEX and launchpads, are occupied by well-known names and assets, as seen on our infographics below:

Still, one particular use case, yield generation and leverage, has been relatively unexplored yet possesses vast potential.
While Solana leads the memecoin race, one project from its ecosystem that expands into this sphere is BlonkFi, a money market protocol where memecoins can be used as collateral to borrow stablecoins. We put BlonkFi to the spotlight in this article to tell you about its core features and benefits.
BlonkFi’s Pre-Seed Round and Testnet Launch
BlonkFi is a new protocol on Solana focused on serving the memecoin market, which completed its pre-seed investment round at the end of July, led by crypto VC firms UOB Venture Management and Signum Capital, with additional participation from DWF Labs and other funds.
The protocol plans to launch in the testnet at the end of September 2024, allowing users to try out the platform and explore its features. The testnet will allegedly support several crypto assets, including WIF, BONK, and MOTHER.
Memecoin Borrowing Mechanism in BlonkFi
BlonkFi is a money market protocol, serving as a tool for collateralisation of memecoins. Users can deposit their memecoins to earn yield, or choose to borrow stables and potentially ape in another token without selling their initial position, which is currently not possible with respect to memecoins in any other dapp.
High price volatility of memecoins is the main issue BlonkFi had to solve to make memecoins useful as collateral. Thus, the developers introduced robust risk management through the Moon and Throttle Modules, to help borrowers mitigate volatility and protect them against downside risks.
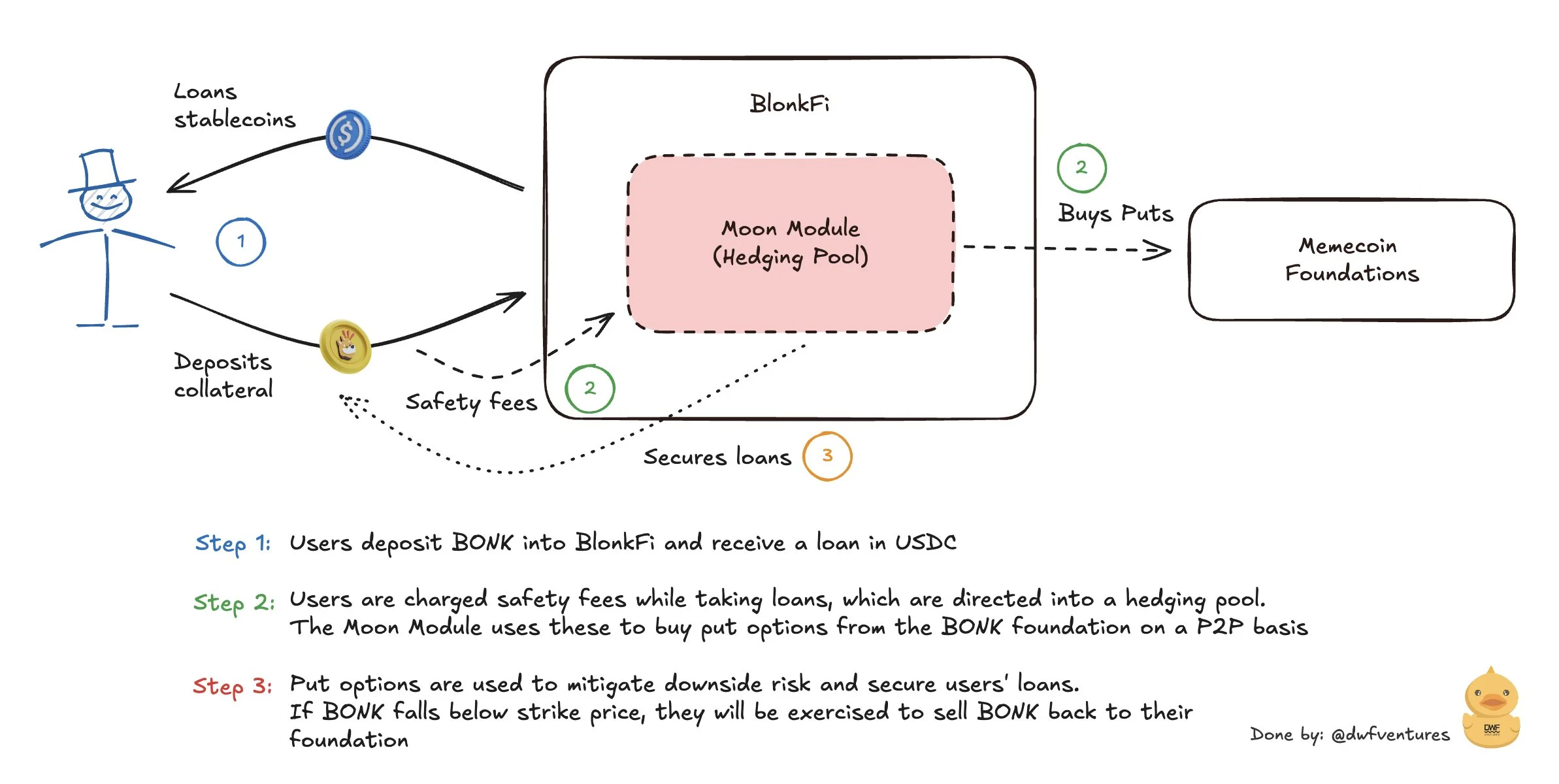
BlonkFi’s Moon Module Explained
Moon Module aims to reduce users' losses in drawdowns, enabling the protocol to retain higher LTV in comparison to competitors. BlonkFi is also the first to introduce direct partnerships with the developers of memecoins, reducing users' liquidations by exercising options in time.
Here is a simple explanation of how the Moon Module works:
- Users provide a meme token BONK as collateral in BlonkFi in exchange for loans denominated in stablecoins (USDC).
- As they take out loans, they are required to pay safety fees. These fees are then directed to a Moon Module, which acts as a hedging pool.
- The Moon Module uses the collected fees to purchase put options from the BONK foundation on a P2P basis. A put option gives the right to sell BONK at a predetermined price if the market price drops below a certain level.
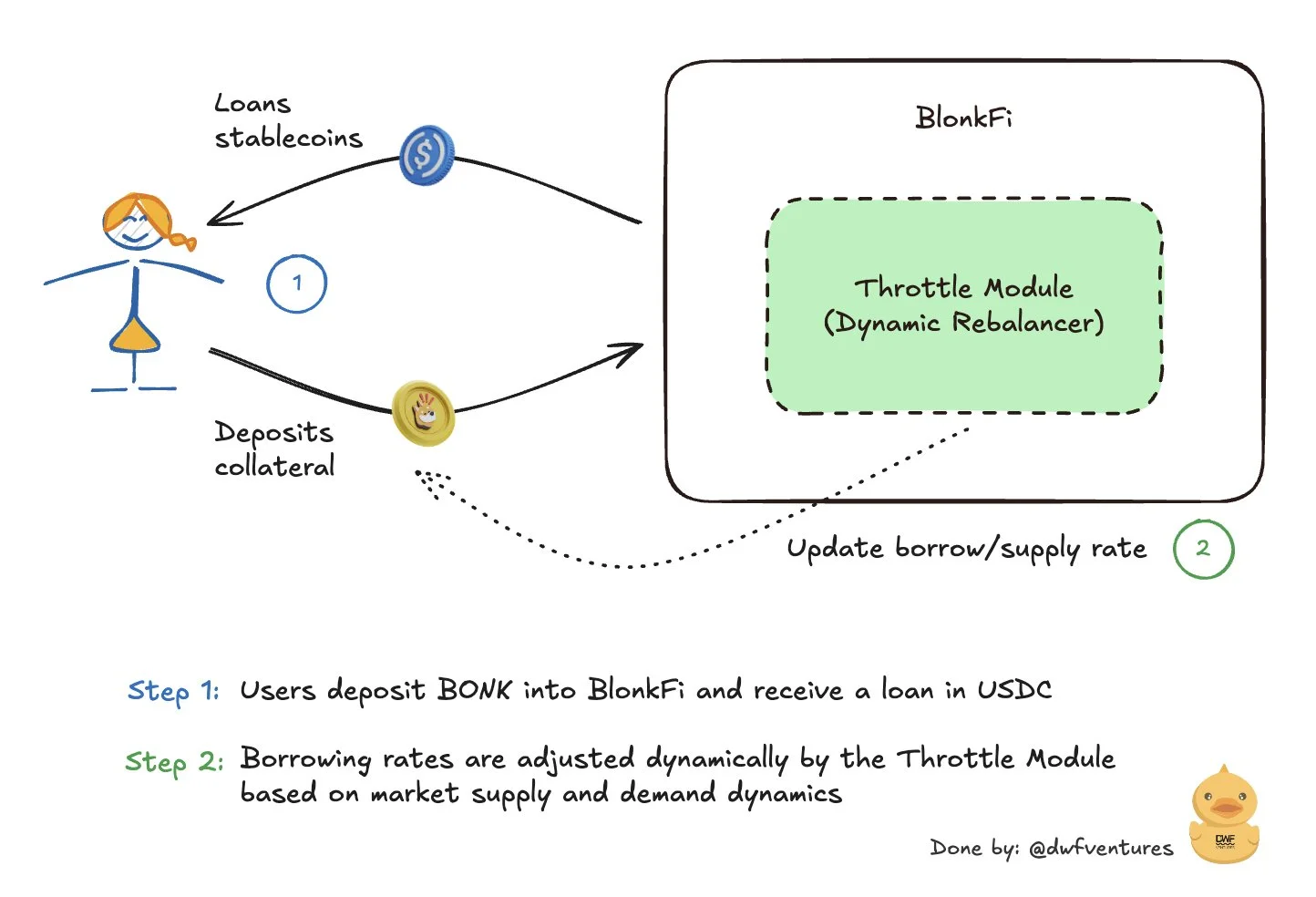
How Does BlonkFi's Throttle Module Work?
Alongside the Moon Module, BlonkFi operates the Throttle Module, needed for adjusting borrowing and supply rates in real-time in response to market conditions. Essentially, its main job is to update the exchange rate between the memecoin provided as collateral and a borrowed stablecoin.
Liquidation Process
When it comes to a money market protocol such as BlonkFi, one of the main concerns is how the liquidation works, what the triggering conditions are, and what happens after the liquidation.
In BlonkFi, the liquidation process involves multiple stages. Here is a short summary:
- Monitoring collateral: The platform continuously tracks the value of the borrower's collateral using real-time price feeds from the Throttle Module and checks the Loan-to-Value (LTV) ratio against set thresholds.
- Liquidation triggering: If the collateral’s value drops, making the LTV ratio too high, a liquidation event starts. The borrower is notified, and BlonkFi sells their collateral, minimising market impact. If needed, the Moon Module may exercise or sell options to cover any shortfall.
- Loan repayment: Proceeds from the collateral sale go toward repaying the crypto loan, with applicable fees deducted. Any leftover funds are returned to the borrower.
- Post-liquidation: If the collateral sale doesn’t cover the full loan, BlonkFi absorbs the loss or follows additional risk management protocols.
Such a common yet practical approach to risk management balances protecting the protocol’s crypto assets while giving borrowers a chance to mitigate potential losses.
Overall
BlonkFi promises to become the first Web3 project to make memecoins a sufficient collateral for stablecoin loans, if it succeeds in managing the high volatility of these kinds of crypto assets.
Being the project’s supporters, we look forward to the launch of BlonkFi as we believe this protocol has the potential to bring a new paradigm of how memecoins can be utilised in DeFi, boosting the overall growth of the sector.
If you build in the MemeFi space and feel like we could collaborate, contact DWF Ventures directly.